In the consumer electronics manufacturing industry, injection molding is the most mature, efficient and cost-effective mass production technology for plastic products. Mobile phone cases, as essential protective and decorative accessories for smartphones, rely heavily on injection molding to achieve consistent quality, precise fit, and diverse designs. Unlike small-batch, customized production methods such as 3D printing, injection molding excels in large-scale manufacturing, enabling the production of thousands of high-quality mobile phone cases per hour while controlling costs. This article will detailedly interpret the core principles of injection molding, the characteristics of injection-molded mobile phone cases, the complete manufacturing process, and key quality control points, revealing how this classic technology supports the mass production of mobile phone accessories.
I. Core Process Interpretation: Injection Molding Adapts to Mobile Phone Case Manufacturing Needs
Injection molding (also known as injection moulding) is a plastic processing technology that melts plastic raw materials and injects them into a closed mold cavity under high pressure, then cools and solidifies to form the desired product shape. For mobile phone cases, which require precise dimensional accuracy (fit with the phone body), smooth surface, and structural stability, injection molding’s "high efficiency, high precision, and high consistency" advantages are perfectly matched. Its core principles, key equipment, and process characteristics are as follows:
1.1 Core Principle of Injection Molding
The core logic of injection molding is "melting - injection - cooling - demolding", which is a cyclic process that can be continuously repeated for mass production. Specifically, the process is divided into four key stages: first, plastic pellets are fed into the barrel of an injection molding machine, where they are heated and melted into a viscous fluid state (melting temperature varies according to plastic material, generally 160-250℃); second, the molten plastic is injected into the pre-designed mobile phone case mold cavity at high pressure (injection pressure is usually 50-150MPa) and high speed, ensuring that the plastic fills every detail of the mold (such as camera cutouts, button holes, and edge contours); third, the molten plastic in the mold cavity is cooled and solidified into the shape of a mobile phone case under the action of a cooling system; finally, the mold is opened, and the finished product is ejected by an ejection mechanism, completing one production cycle. A single cycle usually takes 10-30 seconds, depending on the thickness and material of the mobile phone case.
1.2 Key Equipment for Mobile Phone Case Injection Molding
The injection molding of mobile phone cases relies on two core pieces of equipment: the injection molding machine and the mold. The performance of the equipment directly determines the quality and production efficiency of the mobile phone case:
• Injection Molding Machine: For mobile phone cases, small to medium-sized horizontal injection molding machines (clamping force 50-200 tons) are usually selected. The key components include the feeding system (screw and barrel), heating system, injection system, clamping system, cooling system, and control system. The screw is responsible for conveying, melting, and plasticizing the plastic pellets; the clamping system ensures that the mold is tightly closed during injection to prevent molten plastic leakage; the control system (PLC control) accurately adjusts parameters such as temperature, pressure, and time to ensure stable production.
• Mold (Mobile Phone Case Mold): The mold is the "template" of the mobile phone case, usually made of high-precision steel (such as S136, H13) to ensure wear resistance and dimensional stability. A complete mobile phone case mold consists of a fixed mold (connected to the injection nozzle) and a moving mold (connected to the ejection mechanism). The mold cavity is designed according to the 3D model of the mobile phone case, including details such as the shell contour, camera cutout, charging port, and button positions. The mold also has a cooling water channel to accelerate the cooling and solidification of the molten plastic, improving production efficiency. For mass production, multi-cavity molds (2-cavity, 4-cavity, or 8-cavity) are often used, enabling the production of multiple mobile phone cases in one injection cycle.
1.3 Key Process Advantages (Adapting to Mobile Phone Case Manufacturing)
Compared with other plastic processing technologies (such as 3D printing, vacuum forming), injection molding has four irreplaceable advantages in the mass production of mobile phone cases:
• High Production Efficiency: A single injection cycle is only 10-30 seconds, and multi-cavity molds can produce multiple products at one time. For example, an 8-cavity mold can produce 1600-4800 mobile phone cases per hour, which is far higher than other production methods, meeting the large-scale market demand for mobile phone cases.
• High Precision and Consistency: The dimensional accuracy of injection-molded mobile phone cases can reach ±0.01-0.05mm, ensuring a tight fit with the mobile phone body (no looseness or tightness). The automated production process ensures that each mobile phone case has the same shape, size, and surface quality, avoiding the inconsistency of manual or small-batch production.
• Diverse Material Adaptability: Injection molding can be applied to various plastic materials suitable for mobile phone cases, such as TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), PC (polycarbonate), PC+TPU composite materials, and ABS. Different materials can achieve different characteristics (such as softness, hardness, transparency, and impact resistance), meeting the diverse needs of consumers (such as shockproof, transparent, and matte cases).
• Low Cost in Mass Production: Although the initial investment in molds and injection molding machines is relatively high, the unit cost of each mobile phone case is greatly reduced when the production volume reaches a certain scale (usually more than 10,000 pieces). This is the core reason why most mainstream mobile phone case brands adopt injection molding for mass production.
II. Product Introduction: Injection-Molded Mobile Phone Cases
Injection-molded mobile phone cases are the mainstream products in the current mobile phone accessory market, integrating protection, decoration, and practicality. Compared with mobile phone cases made by other processes, injection-molded products have obvious advantages in fit, durability, and appearance. Their basic specifications, material characteristics, and core advantages are as follows:
2.1 Basic Product Specifications
• Size: Customized according to the model of the mobile phone (such as iPhone 15, Samsung Galaxy S24), the overall size is consistent with the mobile phone body, and the edge thickness is usually 0.8-2.0mm (adjustable according to protection needs). The cutouts (camera, charging port, speaker, button) are precisely aligned with the mobile phone’s functional positions, with an alignment accuracy of ±0.05mm.
• Thickness and Weight: The thickness of the shell is 0.8-1.5mm for ordinary protective cases, and 1.5-2.0mm for shockproof cases; the weight is 10-30g, which is light and does not increase the burden of carrying the mobile phone.
• Surface Quality: The surface is smooth and free of burrs, scratches, or bubbles. According to the design needs, it can be processed into matte, glossy, frosted, or patterned surfaces (such as carbon fiber texture, marble texture).
• Color: Diverse colors are available, including solid colors (black, white, pink), gradient colors, and matte colors. The color is uniform and does not fade easily (achieved by adding color masterbatches during the injection molding process).
2.2 Common Materials for Injection-Molded Mobile Phone Cases
The material of the mobile phone case directly determines its performance (shockproof, scratch-resistant, transparency) and feel. The following are the four most common materials used in injection-molded mobile phone cases, each with its own characteristics:
• TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): A soft plastic material with good elasticity, impact resistance, and wear resistance. It is non-toxic and environmentally friendly, and the case made of TPU is soft and easy to put on and take off, with good shockproof effect (can absorb the impact force when the mobile phone falls). It is suitable for shockproof and soft mobile phone cases, and can also be used as the inner layer of composite cases.
• PC (Polycarbonate): A hard plastic material with high strength, scratch resistance, and transparency. The case made of PC is hard and durable, not easy to deform, and can be made into a fully transparent case (showing the original appearance of the mobile phone). However, it is relatively brittle and has poor impact resistance (easy to break when dropped), so it is often used in combination with TPU.
• PC+TPU Composite Material: The most mainstream material for mobile phone cases. The outer layer is PC (hard, scratch-resistant, transparent), and the inner layer is TPU (soft, shockproof, non-slip). This combination combines the advantages of both materials, achieving both scratch resistance and shockproof performance, and is widely used in middle and high-end mobile phone cases.
• ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A hard plastic material with good impact resistance, rigidity, and processability. It is cheap and suitable for mass production of low-cost mobile phone cases. However, it has poor wear resistance and is not transparent, so it is mostly used in matte or patterned ordinary protective cases.
2.3 Core Advantages of Injection-Molded Mobile Phone Cases
Compared with mobile phone cases made by 3D printing, vacuum forming, or manual pasting, injection-molded mobile phone cases have three core advantages that are widely recognized by the market:
• Perfect Fit: The high precision of injection molding ensures that the case is tightly fitted with the mobile phone body, without gaps or looseness. The cutouts are precisely aligned with the mobile phone’s functional positions, which does not affect the use of the mobile phone’s buttons, charging, or taking photos.
• Durable and Long-Lasting: The injection-molded case has a dense structure, no bubbles or gaps inside, and good wear resistance, impact resistance, and aging resistance. It can be used for a long time without deformation, discoloration, or cracking (under normal use conditions).
• Cost-Effective: For mass production, the unit cost of injection-molded mobile phone cases is very low, which enables brands to provide high-quality products at a reasonable price (usually 10-50 yuan per piece), meeting the consumption needs of most users.
III. Complete Manufacturing Steps: From Mold to Finished Mobile Phone Case
The injection molding of mobile phone cases is a systematic project, which needs to go through "preliminary preparation - mold installation and debugging - injection molding production - post-processing - quality inspection - packaging" six key stages. Each stage has strict operation standards to ensure the quality and efficiency of the product. The complete steps are as follows:
Stage 1: Preliminary Preparation (Core: Lay the Foundation for Stable Production)
Preliminary preparation is the key to avoiding production defects and ensuring stable production efficiency, mainly including three links: mold design and manufacturing, plastic raw material preparation, and equipment inspection, which takes about 3-7 days (the mold manufacturing cycle is the longest).
Step 1: Mold Design and Manufacturing
1. 3D Model Design: According to the 3D size data of the target mobile phone (provided by the mobile phone manufacturer or obtained through reverse engineering), use professional design software (such as Solidworks, UG) to design the 3D model of the mobile phone case, including the shell contour, camera cutout, charging port, button positions, edge thickness, and surface texture. At the same time, design the mold structure (such as cavity number, cooling water channel, ejection mechanism) according to the injection molding process requirements.
2. Mold Manufacturing: The mold is made of high-precision steel (S136 or H13) through processes such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and polishing. The key steps include: processing the mold base (fixed mold and moving mold), machining the mold cavity (according to the 3D model of the mobile phone case, with a surface roughness of Ra≤0.2μm to ensure the smoothness of the mobile phone case surface), drilling the cooling water channel (evenly distributed around the cavity to accelerate cooling), and installing the ejection mechanism (ejector pins or ejector plates) and guide pillars (ensuring the mold is accurately closed).
3. Mold Testing and Adjustment: After the mold is manufactured, install it on a test injection molding machine for trial injection. Check whether the trial product (mobile phone case) has defects such as insufficient filling, burrs, or deformation. If there are defects, adjust the mold (such as modifying the cavity size, optimizing the cooling water channel, or adjusting the ejection mechanism) until the trial product meets the quality requirements.
Step 2: Plastic Raw Material Preparation
1. Material Selection: Select the appropriate plastic material according to the product positioning (such as TPU for soft shockproof cases, PC+TPU for composite cases, and PC for transparent cases). The raw material must meet the requirements of environmental protection (RoHS certification) and non-toxicity (food-grade standard, since the case is in contact with the human hand for a long time).
2. Raw Material Drying: Most plastic pellets (such as PC, ABS) absorb moisture easily, which will cause bubbles or silver streaks in the injection-molded product. Therefore, before use, the plastic pellets need to be dried in a dryer: the drying temperature is 80-120℃, and the drying time is 2-4 hours, until the moisture content of the pellets is ≤0.05%.
3. Color Matching: According to the design requirements, add the corresponding color masterbatch to the dried plastic pellets (the ratio of color masterbatch to plastic pellets is usually 1%-5%). Put the mixed pellets into a mixer and stir evenly to ensure that the color of the finished product is uniform.
Step 3: Equipment Inspection and Debugging
1. Check the injection molding machine: Check whether the screw, barrel, injection nozzle, and clamping system of the injection molding machine are clean and free of residual materials (from previous production). Check the operation status of the heating system, cooling system, and hydraulic system to ensure that the temperature, pressure, and speed can be accurately adjusted.
2. Set initial process parameters: According to the selected plastic material and mold size, set the initial injection molding parameters, including: melting temperature (160-250℃, adjusted according to the material), injection pressure (50-150MPa), injection speed (50-150mm/s), holding pressure (30-80MPa), holding time (2-5 seconds), cooling time (5-20 seconds), and mold opening/closing speed.
Stage 2: Mold Installation and Debugging (Core: Ensure Precise Molding)
This stage is to install the qualified mold on the injection molding machine and adjust the process parameters to ensure that the injection molding process is stable and the product quality meets the requirements, taking about 1-2 hours.
Step 1: Mold Installation
1. Clean the mold surface (fixed mold and moving mold) to remove dust and oil stains, avoiding affecting the fit of the mold and the quality of the product.
2. Use a crane to hoist the mold to the clamping system of the injection molding machine, align the mold base with the installation surface of the machine, and fix it with bolts. Ensure that the mold is installed horizontally and vertically, and there is no deviation.
3. Connect the cooling water channel of the mold to the cooling system of the injection molding machine, and check for water leakage (to ensure the cooling effect is stable).
Step 2: Process Parameter Debugging
1. Start the injection molding machine, heat the barrel to the set melting temperature, and keep it warm for 10-15 minutes (to ensure that the plastic can be fully melted).
2. Perform trial injection: Inject the mixed plastic pellets into the mold cavity, and take out the finished product after cooling and demolding.
3. Adjust parameters according to the trial product: Check the trial product for defects such as insufficient filling (the case is incomplete), excessive filling (burrs on the edge), bubbles (surface or internal), deformation (edge warping), or uneven color. Adjust the parameters accordingly: for example, if there is insufficient filling, increase the injection pressure and speed; if there are burrs, reduce the injection pressure and holding pressure; if there are bubbles, extend the drying time of the raw materials and increase the melting temperature.
4. Repeat trial injection and parameter adjustment until the finished product has no defects, the size is accurate, the surface is smooth, and the fit with the mobile phone body meets the requirements. Record the final process parameters (for subsequent mass production).
Stage 3: Injection Molding Mass Production (Core: Efficient and Stable Output)
After the mold and parameters are debugged, mass production can be carried out. This stage is fully automated, and only a small number of operators are required to monitor the production status, with a production cycle of 10-30 seconds per cycle. The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Raw Material Feeding
Continuously add the dried and color-matched plastic pellets into the feeding hopper of the injection molding machine. The feeding speed is adjusted according to the production efficiency to ensure that there is sufficient raw material in the barrel.
Step 2: Automated Injection Molding Cycle
The injection molding machine automatically completes the following cycle: 1. Feeding: The screw conveys the plastic pellets from the hopper to the barrel; 2. Melting: The heating system melts the plastic pellets into a viscous fluid; 3. Injection: The screw pushes the molten plastic into the mold cavity at high pressure and high speed; 4. Holding: Maintain a certain pressure to supplement the plastic that shrinks during cooling; 5. Cooling: The cooling system cools the molten plastic in the mold cavity to solidify it into a mobile phone case; 6. Mold Opening: The clamping system opens the mold (fixed mold and moving mold separate); 7. Demolding: The ejection mechanism ejects the finished mobile phone case from the mold cavity; 8. Mold Closing: The clamping system closes the mold again, and the next cycle starts.
Step 3: Production Monitoring
Operators regularly check the finished products (every 10-15 minutes) to ensure that there are no defects such as burrs, bubbles, or deformation. At the same time, check the operation status of the injection molding machine and the mold, such as whether the temperature, pressure, and speed are stable, whether the mold has water leakage or material leakage, and whether the ejection mechanism is smooth. If any abnormality is found, stop production immediately and adjust.
Stage 4: Post-Processing (Core: Improve Product Appearance and Quality)
The finished mobile phone case just demolded has some small defects (such as burrs, gate marks) that need to be processed to improve the appearance and feel. The post-processing steps are simple and can be automated or manual, taking about 0.5-1 minute per product.
Step 1: Burr Removal
Use a deburring machine (for mass production) or manual tools (such as a blade, sandpaper) to remove the burrs on the edge of the mobile phone case and the gate mark (the position where the molten plastic enters the mold cavity). Ensure that the edge of the case is smooth and free of sharp corners (to avoid scratching the user’s hand).
Step 2: Surface Treatment (Optional)
According to the design requirements, perform surface treatment on the mobile phone case to improve the appearance and feel. Common surface treatments include: 1. Polishing: Polish the surface of the case to make it more glossy (for transparent PC cases); 2. Frosting: Use a frosting machine to make the surface matte, which is non-slip and not easy to leave fingerprints; 3. Pattern Printing: Print patterns (such as carbon fiber, marble) on the surface of the case using screen printing or UV printing; 4. Plating: Plate a thin layer of metal (such as gold, silver) on the surface of the case to improve the grade (for high-end cases).
Step 3: Cleaning and Drying
Put the processed mobile phone cases into a cleaning machine, use clean water or a neutral cleaning agent to clean the surface dust and oil stains, then dry them in a dryer (temperature 60-80℃, time 10-15 minutes) to ensure that the surface is clean and dry.
Stage 5: Quality Inspection (Core: Ensure Qualified Products Leave the Factory)
Quality inspection is the last line of defense to ensure product quality. Each batch of mobile phone cases must go through strict inspection, and unqualified products are sorted out and reprocessed or scrapped. The key inspection items are as follows:
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Check the appearance of the mobile phone case: no burrs, scratches, bubbles, or color unevenness; the pattern (if any) is clear and does not fade; the edge is smooth and free of sharp corners.
Step 2: Dimensional and Fit Inspection
Use a caliper and a 3D measuring instrument to check the size of the mobile phone case (thickness, length, width) and the size of the cutouts, ensuring that the dimensional accuracy meets the requirements (±0.05mm). At the same time, fit the case on the target mobile phone to check whether it is tight, whether the cutouts are aligned, and whether the buttons can be pressed smoothly.
Step 3: Performance Inspection (Sampling)
Sample inspection is performed on each batch of products (sampling ratio 1%-5%): 1. Impact Resistance Test: Drop the mobile phone with the case from a height of 1.5 meters (simulate daily falling) to check whether the case is cracked or deformed; 2. Wear Resistance Test: Use a wear tester to rub the surface of the case 1000 times to check whether the color fades or the surface is scratched; 3. High-Temperature Resistance Test: Put the case in an oven at 80℃ for 2 hours, then take it out to check whether it is deformed or discolored.
Step 4: Sorting and Handling
Sort out qualified products and unqualified products. Qualified products enter the packaging link; unqualified products (with minor defects such as small scratches) are reprocessed (such as re-polishing), and products with serious defects (such as deformation, cracks) are scrapped.
Stage 6: Packaging (Core: Protect Products During Transportation)
The packaging of mobile phone cases is mainly to protect the products from scratches and damage during transportation and storage, and at the same time improve the product grade. The steps are as follows:
• Individual Packaging: Put each qualified mobile phone case into a transparent plastic bag (OPP bag) to prevent dust and scratches. For high-end cases, a paper box or EVA foam bag can be used for individual packaging.
• Bulk Packaging: Put the individually packaged mobile phone cases into a carton, and add foam or bubble wrap between the cartons to prevent collision during transportation. The number of products per carton is determined according to the size of the case (usually 50-100 pieces per carton).
• Labeling: Paste a label on the carton, indicating the product name, model, material, color, quantity, production date, and batch number, which is convenient for storage, transportation, and after-sales tracking.
IV. Key Quality Control Points and Common Defects Solutions
In the injection molding production of mobile phone cases, quality control is crucial. The following are the key quality control points and solutions to common defects, helping to avoid production problems and improve product qualification rate:
4.1 Key Quality Control Points
• Mold Quality: Regularly maintain and repair the mold (such as polishing the cavity, checking the cooling water channel, and replacing worn ejector pins) to ensure that the mold is in good condition and avoid defects caused by mold wear.
• Raw Material Quality: Strictly inspect the plastic raw materials and color masterbatches to ensure that they meet the environmental protection and performance requirements, and avoid defects caused by unqualified raw materials (such as bubbles, color unevenness).
• Process Parameter Stability: During mass production, strictly control the injection molding parameters (temperature, pressure, speed, time) to avoid parameter fluctuations, which may lead to product inconsistency.
• Post-Processing Quality: Ensure that the burrs are completely removed and the surface treatment is uniform, avoiding affecting the appearance and feel of the product.
4.2 Common Defects and Solutions
• Insufficient Filling: The mobile phone case is incomplete, and some details (such as button holes) are not filled. Solution: Increase injection pressure and speed, raise the melting temperature, extend the holding time, or check whether the mold cavity is blocked.
• Burrs: There are redundant plastic edges on the edge of the case or around the cutouts. Solution: Reduce injection pressure and holding pressure, adjust the mold closing force (increase), or polish the mold cavity to eliminate gaps.
• Bubbles: There are small bubbles on the surface or inside of the case. Solution: Extend the drying time of the raw materials (remove moisture), reduce the melting temperature (avoid overheating), or increase the holding pressure to discharge air in the cavity.
• Deformation: The case is warped or distorted, and cannot fit the mobile phone body. Solution: Optimize the cooling system (extend cooling time, adjust the position of the cooling water channel), adjust the mold temperature, or modify the mold cavity structure (reduce uneven stress).
• Uneven Color: The color of the case is inconsistent, with light and dark areas. Solution: Stir the color masterbatch and plastic pellets evenly, increase the melting temperature (ensure uniform color mixing), or replace the color masterbatch (avoid unqualified color masterbatch).
V. Process Summary and Application Prospect
Injection molding is the core technology for mass production of mobile phone cases, and its "high efficiency, high precision, and low cost" advantages are irreplaceable in the consumer electronics industry. The entire production process of injection-molded mobile phone cases, from mold design and manufacturing, raw material preparation, injection molding production, to post-processing and quality inspection, requires strict control of every link to ensure that the product meets the requirements of fit, durability, and appearance.
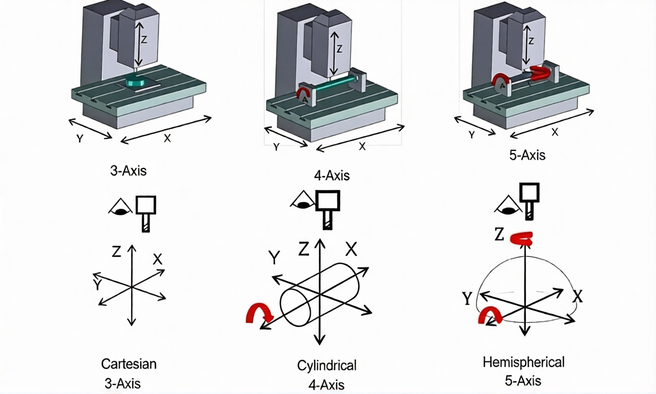
With the continuous development of consumer electronics, the market demand for mobile phone cases is becoming more and more diverse (such as thinner, lighter, more shockproof, and more personalized). This has also promoted the continuous upgrading of injection molding technology: on the one hand, the mold manufacturing technology is more precise (such as 5-axis CNC machining), which can realize more complex surface textures and structural designs; on the other hand, new materials are continuously applied (such as recycled plastic, biodegradable plastic), which meets the environmental protection requirements of the market; in addition, intelligent injection molding equipment (with automatic monitoring, automatic parameter adjustment functions) is gradually popularized, improving production efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
In the future, injection molding will still be the mainstream technology for mobile phone case production. With the integration of intelligent manufacturing, green manufacturing, and personalized design, injection molding will not only meet the mass production needs of mobile phone cases but also support the small-batch customized production of high-end cases, bringing more diverse and high-quality products to consumers. At the same time, the technology will also be applied to the production of other consumer electronic accessories (such as tablet cases, smart watch cases), showing broader application prospects.
Hot Articles
Hot Tags
Manufacturing on Demand
Please fill in the following information to obtain plan details (information is confidential and not disclosed publicly), we will contact you within 24 hours, please keep your phone available!
Upload a 3D/2D model to see instant pricing, lead time, and DFM feedback.