Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding Service
Get custom silicone rubber parts in just days.



Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding Services
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding uses two‑part liquid silicone cured in a heated mold to produce precise, durable parts. The material’s flexibility, heat resistance, and biocompatibility suit demanding applications. The cycle—metering and mixing A/B, injecting into a preheated mold, and high‑temperature curing—yields consistent quality with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
Used across automotive (seals, gaskets, dampers), medical devices (implants, tubing), consumer goods (baby and kitchenware), and electronics (heat‑resistant components), LSR molding ensures biocompatibility, high‑temperature performance, and dimensional accuracy for high‑volume, repeatable production.
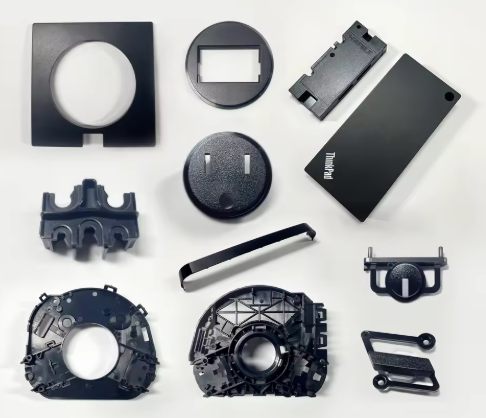

Products of Mastars LSR Injection Molding
LSR Molding Capabilities
Our basic guidelines for LSR molding include important design considerations to help improve part moldability, enhance cosmetic appearance, and reduce overall production time.
| Type | US | Metric | ||
| Size | 12 in. x 8 in. 4 in. | 304.88mm x 203.2mm x 101.6mm | ||
| Volume | 13.3 cu. in. | 217,948 cu. mm | ||
| Depth | No greater than 2 in. from any parting line; deeper parts are limited to a smaller outline | No greater than 50.88mm from any parting line; deeper parts are limited to a smaller outline | ||
| Projected Mold Area | 48 sq. in. | 30968 sq. mm | ||
Liquid Silicone Rubber Materials
✔️ Standard Silicone (30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 durometers)
✔️ Medical-Grade Silicone
✔️ Optical-Grade Silicone
✔️ Fluorosilicone (fuel and oil resistant)
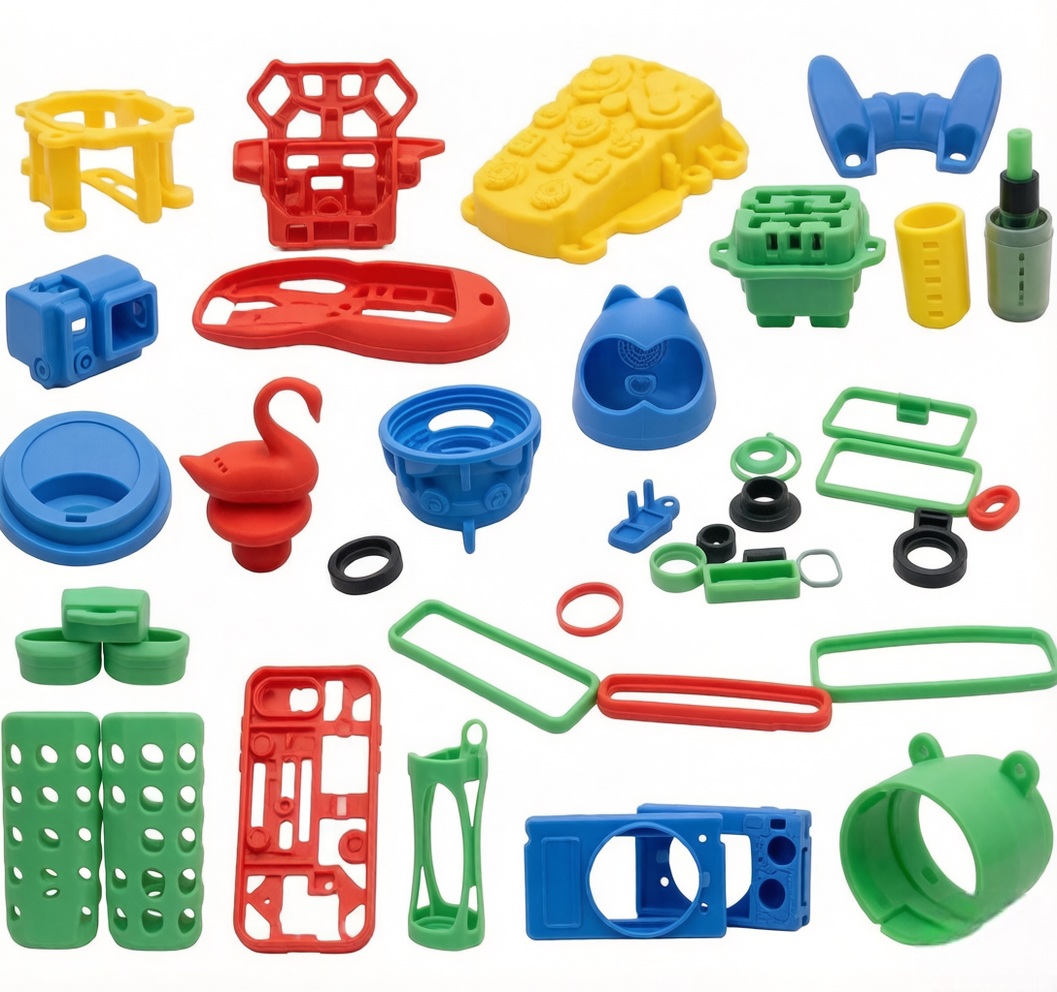


Common applications for LSR Molding
✔️ Low-volume production
✔️ Bridge tooling
✔️ Pilot runs
✔️ Functional prototyping
Our Ideas Have Helped Clients Bring Hundreds Of Products To Market
LSR Injection Molding Design Guidelines
| Feature | Tip | |||
| Undercuts | Reduce undercuts, which will increase the complexity and cost of the tool ejection mechanisms, by adding in pass-thru coring. | |||
| Wall Thickness | Prevent wall sink and voids by maintaining an even wall thickness. Thinner walls reduce cycle time and reduce costs. | |||
| Drafts | Ensure liquid injection molding parts are designed with a minimum draft angle of 0.5°, or up to 5°, for faces with medium textures. | |||
| Ribs/Gussets | Ribs should be 40-60% the thickness of outer walls and should still maintain draft. | |||
| Bosses | Bosses should be designed at a depth of 30% the wall thickness and with a 30% edge groove. Attach them to side walls or ribs for structural integrity. | |||
Key Benefits of LSR Injection Molding
The key benefits of LSR Molding are listed below:
✔️High Precision: Tight tolerances with minimal post‑processing
✔️Flexibility & Durability: Elastic, wear/UV‑resistant, stable
✔️Biocompatibility: Non‑toxic, hypoallergenic, meets FDA/ISO requirements
✔️Efficiency & Cost‑Effectiveness: Fast cycles, automated, low waste
✔️Temperature Resistance: Stable from about -50°C to 230°C

Key Limitations of LSR Injection Molding
The limitations of LSR Molding are listed below.
✔️Material Cost: LSR costs more than common thermoplastics; used only where its properties justify the price.
✔️Limited Applications: Best for small–medium parts; inefficient for large/rigid parts needing high strength.
✔️Mold Complexity: Requires precise temperature control and specialized systems; small deviations raise cost/time.
✔️Longer Cure Times: Curing is slower than thermoplastic cooling, lowering hourly output; tuned via mold temperature and catalyst.
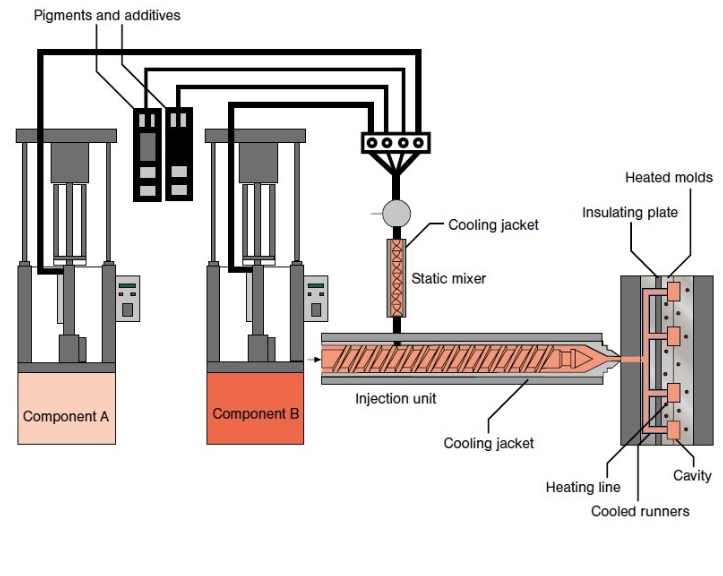
How Does Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Work?
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding uses a two‑part, platinum‑catalyzed system. The base silicone (with vinyl groups) and the crosslinker (with hydride groups) are precisely metered and mixed, then injected into a heated mold where heat triggers crosslinking to form a solid, flexible part. The cycle—mixing, injection under controlled pressure, and thermal curing—yields parts with tight tolerances, smooth surfaces, and consistent quality across runs.
Used in automotive for seals, gaskets, and vibration‑damping components; in medical and consumer health for respiratory masks, tubing, and baby bottle nipples that require biocompatibility and softness; and in electronics for keypads, protective gaskets, and waterproof seals with excellent electrical insulation and flexibility. The process scales efficiently to high‑volume production while maintaining dimensional accuracy and reliability.
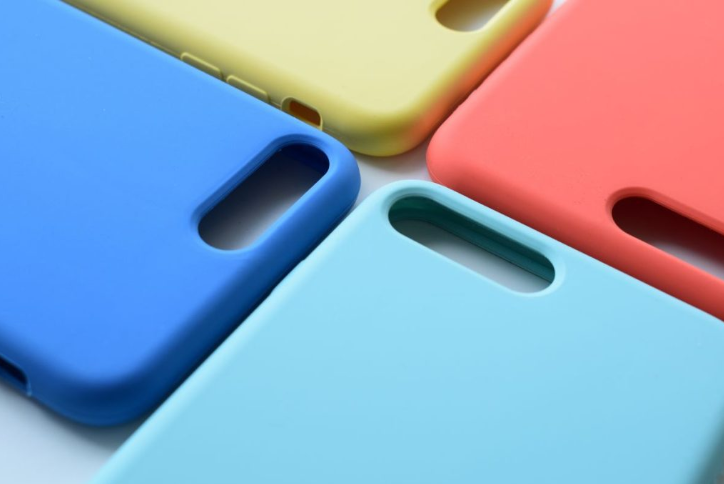

Quality Inspections and Finishing Options
Quality Inspections available for on-demand manufacturing orders
✔️ Designing for Manufacturability (DFM) Feedback
✔️ Scientific Molding Process Development Report
✔️ In-process CMM inspection and machine monitoring
✔️ First article inspection (FAI) and process capability report with GD&T
Certificates
Choose Mastars, You'll Gain
We don't have MOQ, only 1pcs is according to high standard to make, we pursuit the product is perfect to every customer, from 1pcs to million,we are glad to witness and grow together with our customers, that make us proud.


Download Our Manufacturing Equipments List
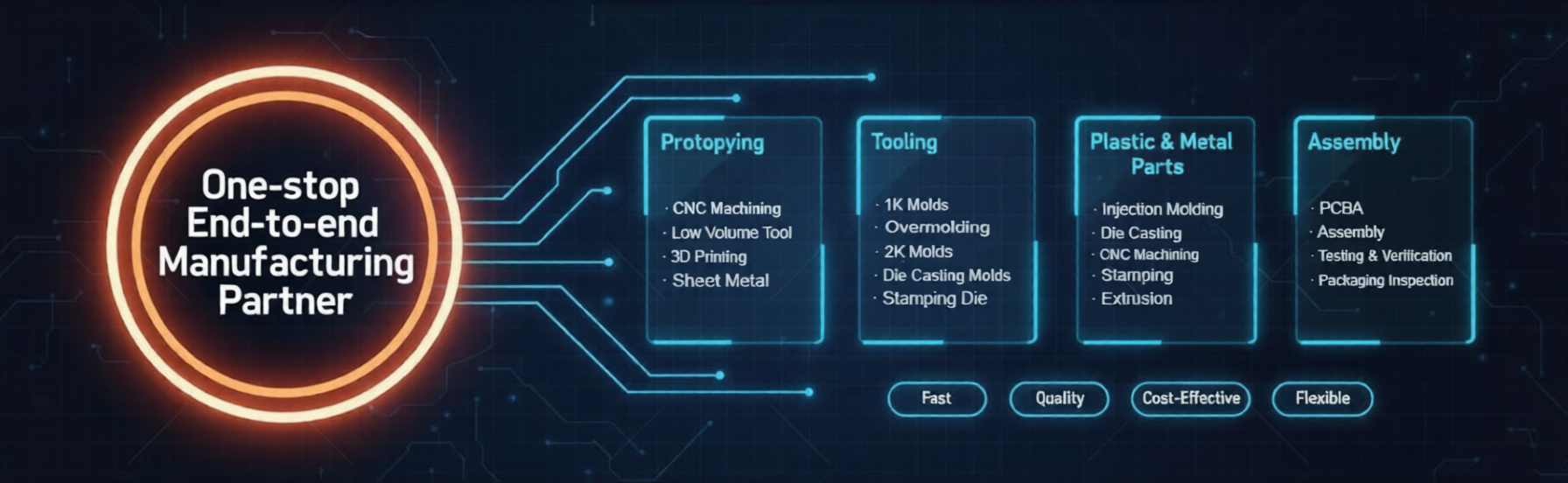
We offer a one-stop processing service from prototypes and molds to machining and assembly, and are equipped with various models of processing equipments from major domestic and international companies, for CNC machining, injection molding, mold making, and sheet metal manufacturing. Download Now!

Our Production Capability
✔️More than 30 injection molding machines of various models
✔️2000T Sets injection machines from 30T to 2000T
✔️ 24H 3*8h shifts Uninterrupted production
✔️ Injection parts precision 0.01mm

Our Services
We don't have MOQ, only 1pcs is according to high standard to make, we pursuit the product is perfect to every customer, from 1pcs to million,we are glad to witness and grow together with our customers, that make us proud.

Industries We Serve
We don't have MOQ, only 1pcs is according to high standard to make, we pursuit the product is perfect to every customer, from 1pcs to million,we are glad to witness and grow together with our customers, that make us proud.

Our Partners
Quick links
Technical video


Manufacturing on Demand
Please fill in the following information to obtain plan details (information is confidential and not disclosed publicly), we will contact you within 24 hours, please keep your phone available!
Upload a 3D/2D model to see instant pricing, lead time, and DFM feedback.