As an efficient and precision metal forming process, Hot Chamber Die Casting has become the core process for mass production of low-melting-point metal components, relying on its core advantages of high efficiency, high automation, and excellent forming precision, and plays an irreplaceable role in various fields such as automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices. Although it has limitations in applicable materials and part size, these limitations are gradually being broken with the continuous upgrading of technology. Similarly, High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC), as a broader and more versatile precision forming technology, integrates the advantages of high efficiency, high precision, and mass production, covering the forming needs of both low-melting-point and high-melting-point metals. It has become the core backbone of the global metal forming industry, driving the upgrading and development of automotive, aerospace, electrical and electronic, and other key industries, and building a solid foundation for the precision and lightweight of industrial products.
I. What is High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)?
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC), referred to as HPDC for short, is a advanced metal forming process that uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a closed mold cavity at high speed, and realizes rapid cooling and solidification to form high-precision, high-density metal components. It is a generalized die casting technology that covers two major branches: Hot Chamber Die Casting and Cold Chamber Die Casting. Its core feature is "high pressure + high speed" — the injection pressure can reach 10-150MPa, and the injection speed can reach 0.5-10m/s, which ensures that the molten metal can quickly and completely fill the mold cavity, accurately replicate the fine structure of the mold, and form components with excellent surface quality and dimensional precision.
Different from other metal forming processes such as forging and casting, High Pressure Die Casting integrates melting, injection, cooling, and forming into one continuous process, which greatly simplifies the production process and improves production efficiency. Its biggest advantage is that it can realize mass production of high-precision metal components with complex shapes, thin walls, and high strength, balancing production efficiency, product quality, and production cost. It is precisely this balance that makes HPDC the preferred process for mass production of metal components in various industries.
It is worth noting that High Pressure Die Casting is not equivalent to Hot Chamber Die Casting or Cold Chamber Die Casting, but a general term for the entire high-pressure injection die casting technology system. Hot Chamber Die Casting is a branch of HPDC suitable for low-melting-point metals, while Cold Chamber Die Casting is another branch suitable for high-melting-point metals. The two complement each other under the framework of HPDC, covering almost all die casting application scenarios of metal materials.
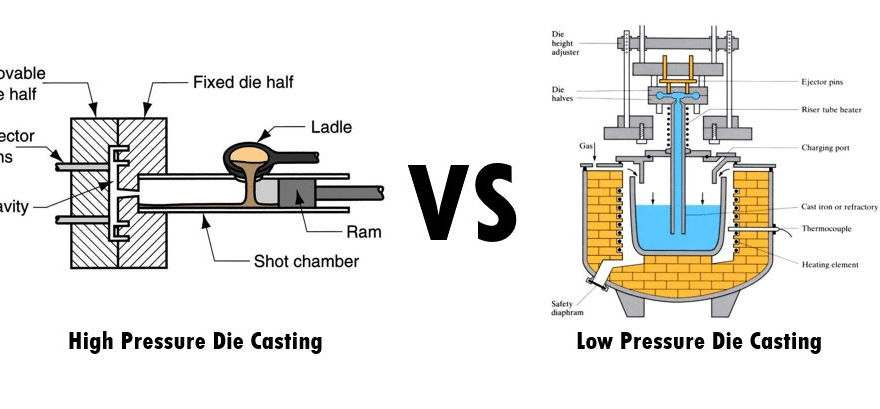
II. Core Structure and Working Principle of High Pressure Die Casting
The working principle of High Pressure Die Casting is based on the "high-pressure injection, rapid solidification" core logic, and its equipment structure is designed to adapt to high-temperature, high-pressure, and high-speed working conditions. The overall structure and working process are highly unified, and the core components and working steps are as follows:
(I) Core Equipment Structure
A complete High Pressure Die Casting machine is mainly composed of six core components, which work together to ensure the stability, efficiency, and precision of the forming process. The structure is slightly different according to the branch (Hot Chamber or Cold Chamber), but the core functions are consistent:
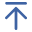
• Melting System: The core device for melting metal raw materials, including furnaces and temperature control components. For Hot Chamber HPDC, the furnace is integrated with the injection chamber; for Cold Chamber HPDC, the furnace is separate from the injection chamber. The melting system can heat different metal materials to the specified molten state (380-1200℃) and keep the temperature stable to ensure the fluidity and purity of the molten metal.
• Injection Mechanism: The core component of HPDC, known as the "heart" of the die casting machine, including the injection chamber, injection plunger, nozzle, and hydraulic drive system. It is responsible for sucking (or receiving) molten metal and injecting it into the mold cavity at high pressure and high speed. The injection plunger is driven by a high-power hydraulic system to realize rapid and stable reciprocating movement, and the injection pressure and speed can be precisely adjusted according to the product requirements.
• Mold Clamping Mechanism: Used to control the opening and closing of the mold and provide sufficient clamping force to resist the high-pressure impact of the molten metal during injection. The clamping force of HPDC machines ranges from tens to thousands of tons, which is matched with the injection pressure and product size. It adopts hydraulic or mechanical drive to ensure that the mold is tightly closed during injection, avoiding mold overflow, deformation, or damage.
• Mold System: Including fixed molds, moving molds, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms. The mold cavity is processed according to the shape of the product, and the cooling channel is used to control the cooling speed of the molten metal in the cavity; the ejection mechanism is responsible for ejecting the formed part from the mold cavity after cooling and solidification. The precision of the mold directly determines the dimensional precision and surface quality of the product.
• Control System: Adopting advanced PLC, touch screen, and intelligent control modules, it is the "brain" of the HPDC machine. It can accurately set and adjust key process parameters such as molten metal temperature, injection pressure, injection speed, clamping force, cooling time, and pressure holding time. High-end models are also equipped with real-time monitoring, fault alarm, and data statistics functions to realize intelligent production and quality control.
• Feeding System: Only configured for Cold Chamber HPDC, used to transfer molten metal from the separate furnace to the injection chamber, including manual feeding (ladle) and automatic feeding (robot, quantitative pouring device). Automatic feeding is widely used in mass production to ensure the consistency of feeding amount and improve production efficiency.
(II) General Working Principle (Complete Process)
Although there are differences in the working details of Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber HPDC, their overall working processes follow the same core logic, which can be divided into 7 standard steps, forming a cyclic production mode:
1. Metal Melting: Put metal raw materials (zinc alloy, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, etc.) into the melting system, heat them to the specified molten state through the heating element, and keep the temperature stable. During the melting process, flux or protective gas is added if necessary to reduce metal oxidation and remove impurities.
2. Mold Preparation and Clamping: Install and debug the mold, check the mold cavity for cleanliness and damage, and ensure that the cooling channel and ejection mechanism work normally. Then, the mold clamping mechanism drives the fixed mold and moving mold to close tightly, and applies sufficient clamping force to lock the mold, preparing for injection.
3. Molten Metal Feeding: For Hot Chamber HPDC, the injection plunger moves upward to form negative pressure, and the molten metal is automatically sucked into the injection chamber; for Cold Chamber HPDC, the molten metal is transferred from the separate furnace to the injection chamber through the feeding system, ensuring that the feeding amount is accurate and uniform.
4. High-Pressure and High-Speed Injection: The injection plunger moves forward rapidly under the drive of the hydraulic system, pushing the molten metal in the injection chamber into the mold cavity at high pressure and high speed. The injection process is divided into slow injection and fast injection stages to avoid air entrainment and ensure that the molten metal fills every corner of the cavity.
5. Pressure Holding and Solidification: After the mold cavity is filled with molten metal, the injection plunger maintains a certain pressure to compensate for the shrinkage of the molten metal during cooling and solidification, ensuring that the internal structure of the product is dense and free of shrinkage holes and air bubbles. At the same time, the cooling system works to accelerate the cooling and solidification of the molten metal in the cavity.
6. Mold Opening and Part Ejection: After the product is completely cooled and solidified, the mold clamping mechanism drives the mold to open, and the ejection mechanism ejects the formed product from the mold cavity. The ejection speed and force are precisely controlled to avoid product deformation or damage.
7. Post-Processing and Inspection: Take out the ejected product, remove the gate, runner, burrs, and other excess parts through post-processing (grinding, cutting, etc.), then inspect the product’s dimensional precision, surface quality, and internal defects. Qualified products enter the next process, while unqualified products are recycled and remelted to reduce waste.
III. Process Characteristics of High Pressure Die Casting (Advantages and Limitations)
High Pressure Die Casting, as a comprehensive precision forming technology, inherits the advantages of its two branches (Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber) and has unique process characteristics. It has obvious advantages in mass production of high-precision metal components, but also has certain limitations, which need to be reasonably selected according to product requirements and application scenarios.
(I) Core Advantages
1. High Production Efficiency, Suitable for Mass Production: HPDC integrates melting, injection, forming, and cooling into one continuous process, with a short production cycle (each cycle takes 5-60 seconds, depending on the product size and material). It can produce hundreds to thousands of products per hour, which is much higher than other metal forming processes such as forging and sand casting. It is especially suitable for large-scale mass production of standard metal components.
2. Excellent Product Precision and Surface Quality: Under the action of high pressure and high speed, the molten metal can accurately replicate the fine structure of the mold cavity. The dimensional tolerance grade of the formed product can reach IT9-IT13, the surface roughness can be as low as Ra≤1.6μm, and the product surface is smooth and flat. Most products can be directly used for assembly without a lot of post-processing, reducing production costs.
3. Wide Adaptability to Materials: As a generalized technology, HPDC covers the forming needs of most die casting metals. Through the combination of Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber branches, it can process low-melting-point metals (zinc alloy, magnesium alloy, lead alloy) and high-melting-point metals (aluminum alloy, copper alloy, brass), as well as some special alloys, meeting the material needs of different industries.
4. High Product Density and Mechanical Properties: The high-pressure injection and pressure holding process can effectively eliminate air bubbles and shrinkage holes in the molten metal, making the internal structure of the product dense. The tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance of the product are significantly higher than those of traditional casting products, which can meet the performance requirements of load-bearing, wear-resistant, and high-temperature-resistant components.
5. Strong Ability to Form Complex Shapes: HPDC can form metal components with complex shapes, thin walls, and fine structures that are difficult to be formed by other processes. The minimum wall thickness of the product can reach 0.5mm, and it can realize the integration of multiple structures, reducing the number of parts and assembly links, and improving the reliability of the product.
6. High Automation and Low Labor Intensity: The entire production process of HPDC can be realized with full automation, including mold clamping, injection, feeding, part taking, and post-processing. It greatly reduces manual intervention, lowers the labor intensity of operators, and avoids errors caused by manual operation, improving product consistency and qualification rate.
(II) Limitations
1. High Initial Equipment and Mold Investment: HPDC machines and molds have high manufacturing precision and complex structure, especially high-pressure, large-tonnage models and precision molds. The initial purchase, installation, and debugging costs are very high, which increases the access threshold for small and medium-sized enterprises. At the same time, the mold manufacturing cycle is long, which is not suitable for small-batch and customized production.
2. Limited Product Size and Weight: Although HPDC has a large forming capacity, it is still limited by the clamping force of the die casting machine and the capacity of the injection chamber. Generally, it is suitable for producing small and medium-sized components (weight 0.1g-100kg, size within 1.5m). For extra-large and extra-heavy metal components, other forming processes such as sand casting and forging need to be adopted.
3. Oxide Inclusions are Easy to Generate: During the injection process, the molten metal is in contact with air, which is easy to oxidize and generate oxide inclusions, especially for Cold Chamber HPDC. The feeding link increases the contact time between molten metal and air, which may affect the internal quality and service life of the product. It is necessary to take additional measures to reduce oxidation, increasing production costs.
4. Difficult Post-Processing of Internal Defects: If the product has internal defects such as air bubbles and shrinkage holes, it is difficult to repair through post-processing. Once unqualified, it can only be recycled and remelted, which may cause waste of raw materials and production costs.
5. High Requirements for Operators and Maintenance: HPDC involves multiple links such as material melting, parameter control, and mold maintenance. Operators need to have professional technical knowledge and rich operation experience to accurately control key process parameters and handle production faults. At the same time, the equipment and mold need regular maintenance and replacement, which increases the maintenance cost and workload.
IV. Key Process Parameters Control of High Pressure Die Casting
The product quality of High Pressure Die Casting is closely related to the control of key process parameters. The "high pressure + high speed" characteristics determine that the parameter control is more strict. Any deviation may lead to product defects such as air bubbles, shrinkage holes, cold shut, material shortage, and deformation. The core parameters that need to be focused on are as follows, covering both Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber HPDC:
(I) Temperature Control
Temperature is the core parameter affecting the fluidity of molten metal and the solidification quality of products, including molten metal temperature and mold temperature:
• Molten Metal Temperature: It is set according to the metal material. For low-melting-point metals (zinc alloy), it is 380-420℃; for medium-melting-point metals (aluminum alloy), it is 650-720℃; for high-melting-point metals (copper alloy), it is 900-1100℃. Excessively high temperature will accelerate oxidation, increase oxide inclusions, and cause product burning; excessively low temperature will reduce fluidity, leading to material shortage and cold shut.
• Mold Temperature: It is usually controlled at 150-300℃, which needs to be kept uniform and stable. For thin-walled products, the mold temperature can be appropriately increased to avoid rapid cooling and cold shut; for thick-walled products, the mold temperature can be appropriately reduced to accelerate cooling and improve production efficiency. The mold temperature is adjusted through the built-in cooling channel and heating device.
(II) Injection Pressure and Speed Control
Injection pressure and speed are the core characteristics of HPDC, which directly affect the filling effect and internal quality of products:
• Injection Pressure: The range is 10-150MPa. For Hot Chamber HPDC (low-melting-point metals), the pressure is 10-50MPa; for Cold Chamber HPDC (high-melting-point metals), the pressure is 50-150MPa. Higher pressure ensures that the molten metal fills the cavity completely and the product is dense, but excessive pressure will cause mold overflow and product deformation.
• Injection Speed: The range is 0.5-10m/s. It is divided into slow injection and fast injection stages. Slow injection (0.1-1m/s) is used to push the molten metal to the nozzle smoothly and avoid air entrainment; fast injection (2-10m/s) is used to fill the mold cavity quickly and reduce cold shut. The speed switching time needs to be accurately controlled to ensure the filling effect.
(III) Pressure Holding Time and Cooling Time Control
• Pressure Holding Time: It is 5-20 seconds, which is used to compensate for the shrinkage of the molten metal during cooling and solidification. Thicker products require longer pressure holding time to ensure that the internal structure is dense and free of shrinkage holes; thin-walled products can shorten the pressure holding time to improve production efficiency.
• Cooling Time: It accounts for 50%-80% of the entire production cycle, ranging from 3-60 seconds. It is determined by the product thickness and material. The cooling time must be sufficient to ensure that the product is completely solidified before mold opening, avoiding deformation and cracks; excessive cooling time will reduce production efficiency.
(IV) Other Key Parameters
• Clamping Force: It needs to match the injection pressure and product size to ensure that the mold is tightly closed during injection. Insufficient clamping force will cause mold overflow; excessive clamping force will increase energy consumption and mold wear.
• Feeding Amount: For Cold Chamber HPDC, the feeding amount must be accurate. Too much feeding will cause mold overflow and increase burrs; too little feeding will cause material shortage. Automatic quantitative feeding is usually used to ensure consistency.
V. Industrial Application Scenarios of High Pressure Die Casting
With the core advantages of high efficiency, high precision, wide material adaptability, and strong complex shape forming ability, High Pressure Die Casting has become an indispensable core process in various industries, covering automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, medical devices, heavy machinery, and other fields. It is widely used in the production of metal components that require mass production, high precision, and high performance. The typical application scenarios are as follows:
(I) Automotive Industry (Largest Application Field)
The automotive industry is the largest application field of HPDC, accounting for more than 70% of the global HPDC market. With the trend of automotive lightweight and electrification, aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, and magnesium alloy components produced by HPDC are widely used in engines, transmissions, chassis, and bodies:
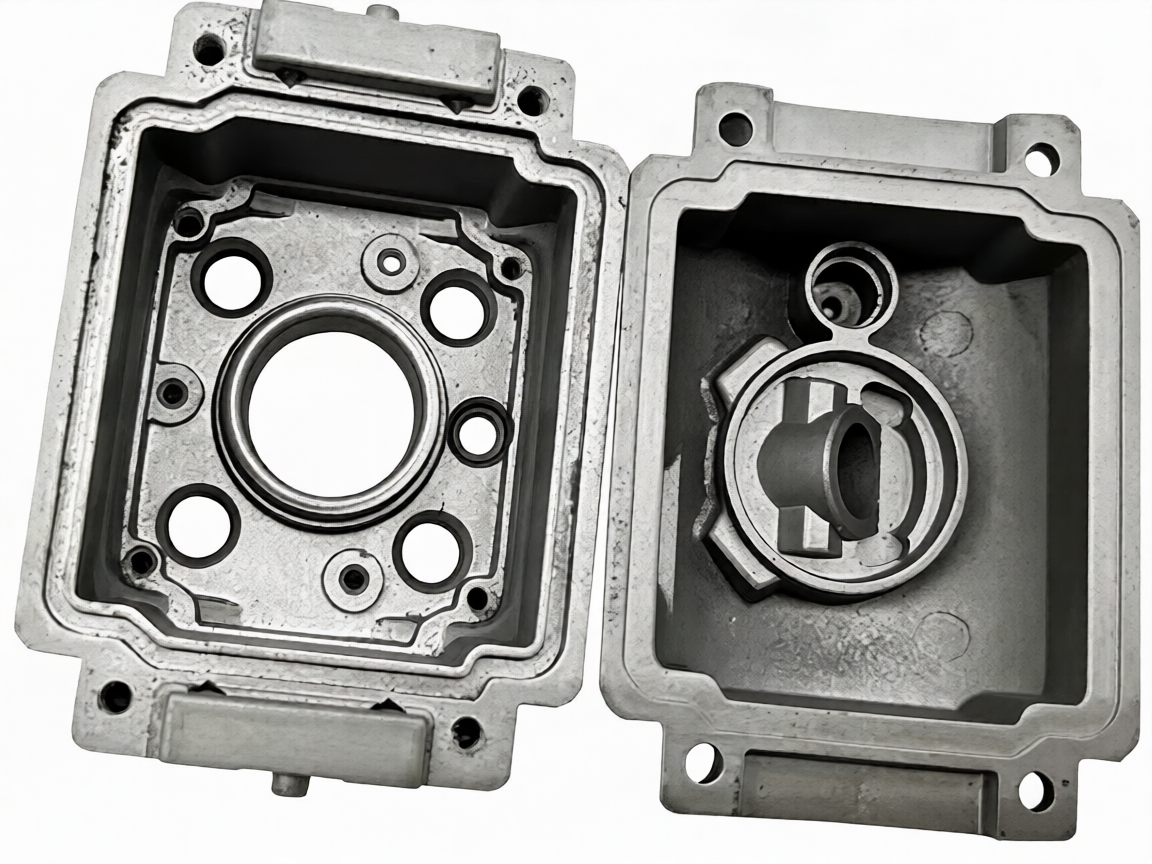
• Engine and Transmission Components: Cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, crankcases, transmission cases, differential cases, etc. These components require high strength, high temperature resistance, and good sealing performance, which are perfectly matched with HPDC’s process advantages.
• Chassis and Body Components: Suspension brackets, steering knuckles, door frames, engine hood frames, battery cases (for new energy vehicles), etc. HPDC realizes the integration of complex structures, reduces the number of parts, and reduces the weight of the vehicle body.
• Interior and Exterior Components: Door handles, instrument panel brackets, air conditioning outlets, car logos, etc. These components require good surface quality and precision, and HPDC can meet the aesthetic and assembly requirements.
(II) Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry has extremely high requirements for the precision, strength, and reliability of metal components. HPDC is widely used in the production of small and medium-sized precision components of aircraft, rockets, and satellites, mainly using high-strength aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, and copper alloy:
• Aircraft Components: Engine brackets, landing gear accessories, hydraulic system connectors, cabin structural parts, etc. These components need to have a high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, and HPDC can ensure strict quality standards.
• Rocket and Satellite Components: Engine nozzles, fuel tank accessories, satellite structural parts, etc. HPDC can form components with complex shapes and high precision, ensuring the stability of aerospace equipment during launch and operation.
(III) Consumer Electronics and Electrical Field
The consumer electronics and electrical field has high requirements for the miniaturization, precision, and lightweight of components. HPDC (mainly Hot Chamber branch) is widely used in the production of metal components of mobile phones, computers, electrical appliances, and other products:
• Consumer Electronics Components: Mobile phone middle frames, camera brackets, key housings, laptop casings, mouse shells, etc. These components require small size, high precision, and good surface quality, and HPDC can realize mass production at low cost.
• Electrical Components: High-voltage switch housings, transformer shells, motor end covers, compressor shells, etc. These components require good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, and HPDC with copper alloy or aluminum alloy is the preferred choice.
(IV) Medical Device Industry
The medical device industry has strict requirements for the precision, cleanliness, and safety of components. HPDC (mainly Hot Chamber branch) is used to produce small precision metal components of medical devices, using environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and biocompatible materials (lead-free zinc alloy, magnesium alloy):
• Diagnostic Equipment Components: Handheld diagnostic instrument housings, detection probe brackets, internal connectors, etc. These components require high precision and no impurities to ensure the stability of the equipment.
• Surgical and Rehabilitation Equipment Components: Small surgical instrument handles, syringe push rods, wheelchair connectors, prosthetic structural parts, etc. These components require smooth surfaces, no burrs, and high durability.
(V) Other Fields
In addition to the above fields, HPDC is also widely used in heavy machinery, hardware tools, marine engineering, and other fields:
• Heavy Machinery: Excavator bucket teeth, hydraulic cylinder blocks, gearbox cases, etc., which require high strength and wear resistance.
• Hardware Tools: Wrench bodies, pliers handles, hammer heads, etc., which can be mass-produced with high efficiency and low cost.
• Marine Engineering: Marine engine components, ship hull connectors, etc., which require good corrosion resistance and high strength.
VI. Development Trends of High Pressure Die Casting
With the continuous development of global manufacturing towards intelligence, greenization, precision, and high efficiency, High Pressure Die Casting, as a core metal forming process, is constantly upgrading and optimizing, breaking through existing limitations, and expanding application boundaries. In the future, it will mainly show the following five development trends:
(I) Intelligence and Automation Upgrade
The integration of industrial robots, machine vision, AI algorithms, and the Internet of Things will make HPDC realize full-process intelligent production. Intelligent control systems can real-time monitor process parameters, automatically adjust parameters according to production status, predict and diagnose faults, and improve production efficiency and product consistency. At the same time, automated production lines will replace manual operations in feeding, part taking, post-processing, and inspection, reducing labor costs and errors.
(II) Precision and Lightweight Development
With the increasing demand for high-precision and lightweight products in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics fields, HPDC will develop towards higher precision and thinner walls. By optimizing mold design (using 3D printing technology to produce complex precision molds), improving injection control precision, and adopting new materials, the dimensional tolerance grade of products can be improved to IT8 or above, and the wall thickness can be reduced to 0.3mm, realizing the integration of precision and lightweight.
(III) Green and Energy-Saving Transformation
Under the background of global carbon neutrality, green and energy-saving has become an important development direction of HPDC. Energy-saving melting furnaces and heat insulation materials will be widely used to reduce energy consumption; molten metal recycling technology will be optimized to improve the utilization rate of raw materials (up to 98% or more); environmentally friendly fluxes and protective gases will be used to reduce oxide emissions; and recyclable materials will be adopted to realize green production.
(IV) Expansion of Material and Application Boundaries
With the development of material science and mold technology, HPDC will gradually expand the applicable material range, and can process high-performance special alloys (titanium alloy, magnesium-lithium alloy) that were difficult to process in the past, meeting the needs of high-end fields such as aerospace and military industry. At the same time, it will expand to new fields such as new energy (wind power, photovoltaic) and 3C electronics, further expanding the application space.
(V) Integration of New Technologies
New technologies such as 3D printing, digital simulation, and bionic design will be integrated with HPDC. 3D printing technology can quickly produce complex molds, shortening the mold manufacturing cycle; digital simulation technology can simulate the injection and solidification process, predict product defects, and optimize process parameters; bionic design can optimize the product structure, improve product performance, and reduce material consumption.
VII. Conclusion
As an efficient and precision metal forming process, Hot Chamber Die Casting has become the core process for mass production of low-melting-point metal components, relying on its core advantages of high efficiency, high automation, and excellent forming precision, and plays an irreplaceable role in various fields such as automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices. Although it has limitations in applicable materials and part size, these limitations are gradually being broken with the continuous upgrading of technology. On this basis, High Pressure Die Casting, as a comprehensive and versatile precision forming technology system, integrates the advantages of Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber Die Casting, covering the forming needs of most metal materials and product types. It has become the core backbone of the global metal forming industry, providing efficient, high-quality, and economical forming solutions for various industries.
Despite the limitations of high initial investment and high technical requirements, with the continuous integration of intelligence, greenization, and new technologies, High Pressure Die Casting will gradually break through these limitations, achieve higher precision, higher efficiency, and greener production. It will not only promote the upgrading and development of automotive, aerospace, and other key industries but also play an important role in the global manufacturing transformation and upgrading, helping the manufacturing industry move towards high-end, high-value-added, and sustainable development. For enterprises, mastering the core technology and parameter control of High Pressure Die Casting will become the key to enhancing core competitiveness and seizing market opportunities in the fierce industrial competition.
Hot Articles
Hot Tags
Manufacturing on Demand
Please fill in the following information to obtain plan details (information is confidential and not disclosed publicly), we will contact you within 24 hours, please keep your phone available!
Upload a 3D/2D model to see instant pricing, lead time, and DFM feedback.