Magnesium die casting technology has become a key process for the lightweight upgrading of new energy vehicles, relying on the core advantages of magnesium alloy such as high specific strength, significant lightweight effect and excellent thermal conductivity. As a core component of the three-electric system of new energy vehicles, the drive motor housing undertakes important functions of fixing the motor, heat dissipation, sealing protection and load transmission, and has strict requirements on weight reduction effect, structural strength, thermal conductivity and dimensional accuracy. Although traditional aluminum alloy housings can meet basic needs, their lightweight potential is close to the bottleneck. Magnesium die casting, through precision forming technology, can achieve extreme weight reduction while ensuring performance, meeting the core demand of extending the range of new energy vehicles. Taking the drive motor housing of pure electric passenger cars as the target product, this article elaborates on the application details, technical points and practical value of magnesium die casting technology, providing a reference for the production of similar magnesium die cast components.
I. Product Characteristics and Compatibility with Magnesium Die Casting Technology
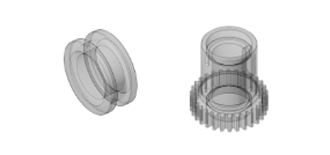
The drive motor housing of the pure electric passenger car in this case is a cylindrical composite structure with an overall size of 280mm×220mm×150mm, an average wall thickness of 3mm and a local heat sink wall thickness of 1.8mm. The inner wall of the housing integrates a motor stator mounting platform and bolt fixing seats, with 8 high-precision mounting holes reserved. The hole position tolerance is ≤0.02mm, which directly affects the motor assembly accuracy and operation stability. The product must withstand vibration and torque generated by high-speed motor operation, requiring a tensile strength of ≥240MPa and a Brinell hardness of ≥75HB. Meanwhile, it must have excellent thermal conductivity (thermal conductivity ≥100W/(m·K)) to quickly dissipate the heat generated by the motor during operation and avoid overheating failure.
Magnesium die casting technology is highly compatible with product requirements: AZ91D magnesium alloy is selected as the raw material, which is mainly composed of magnesium, aluminum and zinc, with a density of only 1.8g/cm³, 30% lighter than aluminum alloy. It can reduce the weight of the motor housing by 2.2kg compared with the aluminum alloy version, helping the whole vehicle reduce weight and energy consumption and extend the driving range. AZ91D magnesium alloy has excellent fluidity, which can accurately fill complex and small structures such as heat sinks. The die casting forming precision reaches IT8-IT10 grade, and the surface roughness Ra≤1.6μm, which can meet assembly requirements without extensive subsequent processing. After T6 heat treatment, the mechanical properties of the material are significantly improved, and its thermal conductivity is much higher than that of cast iron and steel. It can quickly transfer motor heat, and cooperate with heat dissipation structure design to reduce the motor operating temperature by 5-8℃, improving operation stability.
II. Key Design Points of Magnesium Die Casting Mold for Motor Housing
The mold is the core of magnesium die casting forming. It needs to combine the characteristics of magnesium alloy such as easy oxidation and fast solidification speed, taking into account forming precision, heat dissipation efficiency, exhaust effect and mold life. The overall mold adopts a two-plate structure suitable for horizontal cold chamber die casting machines, and the mold material is H13 hot work die steel. After quenching and tempering treatment, nitriding treatment and surface coating treatment, its high-temperature wear resistance, thermal fatigue resistance and oxidation resistance are improved. The core design points are as follows:
Cavity and core design: The cavity adopts an integral structure, which is precisely processed according to the shape of the motor housing. The heat sink area on the inner wall adopts an insert design, and the insert is made of SKD61 material, which is convenient for replacement after wear in the later period and improves the forming precision of the heat sink. The core surface is polished, and a 0.05mm draft angle is reserved to avoid casting sticking to the mold. The fit gap between the cavity and core is controlled at 0.01-0.015mm to prevent flash and adapt to the solidification shrinkage characteristics of magnesium alloy.
Gating and exhaust system: A side gate + annular runner gating system is adopted, with a main sprue diameter of 15mm. The annular runner is attached to the bottom of the cavity to make the magnesium alloy liquid evenly wrap the core, avoiding structural defects caused by excessive local impact. The exhaust system is arranged along the cavity end, heat sink gap and parting surface, with exhaust grooves of 0.2-0.3mm in width and 0.04-0.08mm in depth. Meanwhile, 3 exhaust pins are set at the highest point of the cavity to quickly discharge air and magnesium alloy liquid volatiles in the cavity, preventing air holes and oxidation inclusion defects, and controlling the defect rate below 0.5%.
Cooling system: A zoned closed-loop cooling design is adopted. Spiral water channels are arranged on both the outer wall of the cavity and the inside of the core, with a water channel spacing of 10-12mm. The water temperature is precisely controlled at 25-35℃ by a constant temperature cooling machine to ensure uniform temperature in all areas of the mold, accelerate the solidification of magnesium alloy liquid, control the forming cycle within 90 seconds, and avoid casting deformation caused by uneven cooling.
III. Magnesium Die Casting Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The magnesium die casting of the motor housing follows the full-process control of "raw material pretreatment - die casting forming - heat treatment - post-processing - quality inspection", focusing on preventing and controlling defects such as magnesium alloy oxidation and air holes to ensure that product performance meets the standards. The specific process is as follows:
Raw material pretreatment and die casting forming: AZ91D magnesium alloy ingots are melted at high temperature (650-670℃). During the melting process, a mixed gas of SF₆ and CO₂ is introduced for protection to prevent oxidation and combustion of magnesium alloy. Meanwhile, refining agent is added to remove impurities and gases, improving the purity of molten metal. A 2000kN horizontal cold chamber die casting machine is used for forming, with the following core parameters set: injection pressure 70-90MPa, injection speed 3-5m/s, mold temperature 150-180℃, holding pressure time 2-3s, and cooling time 40-50s. During die casting, the molten metal temperature, injection pressure and mold temperature are monitored in real time through an automatic system, and parameters are accurately adjusted to avoid defects.
Heat treatment and post-processing: After demolding, the gate, riser and flash are first removed, and the surface impurities are cleaned by mechanical grinding and high-pressure air blowing. Then T6 heat treatment is performed (solution treatment at 415℃ for 4 hours, aging treatment at 160℃ for 12 hours after quenching) to eliminate die casting residual stress and improve material mechanical properties. In the post-processing stage, precision reaming is performed on the mounting holes to further improve hole position accuracy. Finally, anodizing process is adopted to form a dense oxide film on the surface, improving corrosion resistance and meeting the requirements of complex working conditions of new energy vehicles.
Quality inspection: Appearance inspection combines visual inspection and optical projector to check for defects such as air holes, cracks and oxidation inclusions, with the defect qualification rate controlled above 99.6%. Dimensional inspection uses a coordinate measuring machine to fully inspect 12 key dimensions including the outer diameter, length and hole spacing of the housing, and all deviations meet the requirements. For mechanical performance sampling, 5 samples are selected per batch, and both tensile strength and hardness meet the standards. Thermal conductivity test shows that the product's thermal conductivity reaches 105W/(m·K), meeting heat dissipation needs. Sealing performance test uses 0.3MPa compressed air, and no leakage within 30s of pressure holding is considered qualified.
IV. Application Value and Practical Effects
After the magnesium die casting drive motor housing is put into production, the single-shift output reaches 800 pieces, which is 15% higher than that of traditional aluminum alloy die casting. Although the unit product production cost is slightly higher than that of aluminum alloy, the comprehensive cost performance advantage is significant due to the extended range achieved by the whole vehicle weight reduction, successfully adapting to the mass production demand of 120,000 pure electric passenger cars per year. The product weight is reduced by 32% compared with the aluminum alloy housing, which can reduce the energy consumption of each vehicle by about 5% and extend the driving range by 8-10km, perfectly meeting the lightweight upgrading demand of new energy vehicles.
Actual vehicle mounting verification shows that the magnesium die casting motor housing has excellent heat dissipation effect. The motor temperature stabilizes below 85℃ after 2 hours of continuous operation, and the operating noise is reduced by 2dB compared with the aluminum alloy version. Its structural strength can withstand the torque and vibration generated by high-speed motor operation, and no deformation or damage occurs after 200,000km road test, meeting the whole vehicle reliability requirements. Meanwhile, the recyclability rate of magnesium alloy materials is over 98%, with low pollutant emissions during production, conforming to the concept of green manufacturing.
Conclusion
With its core advantages of extreme lightweight and high performance, magnesium die casting technology provides an optimal forming solution for the drive motor housing of new energy vehicles. Through scientific raw material selection, mold design, parameter regulation and full-process quality control, it successfully solves the problems of easy oxidation and difficult defect control in magnesium alloy die casting, realizing the high-performance forming of the motor housing. With the reduction of magnesium alloy material cost and the iteration of die casting technology, magnesium die casting technology will be widely applied in more components such as new energy vehicle battery trays and electronic control housings, providing core support for the lightweight and green upgrading of the automotive industry.
Hot Cases
Hot Tags
Manufacturing on Demand
Please fill in the following information to obtain plan details (information is confidential and not disclosed publicly), we will contact you within 24 hours, please keep your phone available!
Upload a 3D/2D model to see instant pricing, lead time, and DFM feedback.