










High-pressure die casting (HPDC) has long been a backbone of manufacturing, particularly for mass-producing complex metal components in sectors like automotive, medical devices, and household appliances. Yet, traditional HPDC grapples with a persistent challenge: uneven cooling in die casting molds. This issue often leads to costly defects—such as warping, shrinkage, and porosity—and extended production cycle times. Enter additive-manufacturing-enabled conformal cooling high-pressure die casting: a revolutionary synergy of technologies that solves these pain points and redefines efficiency and quality in metal component production.
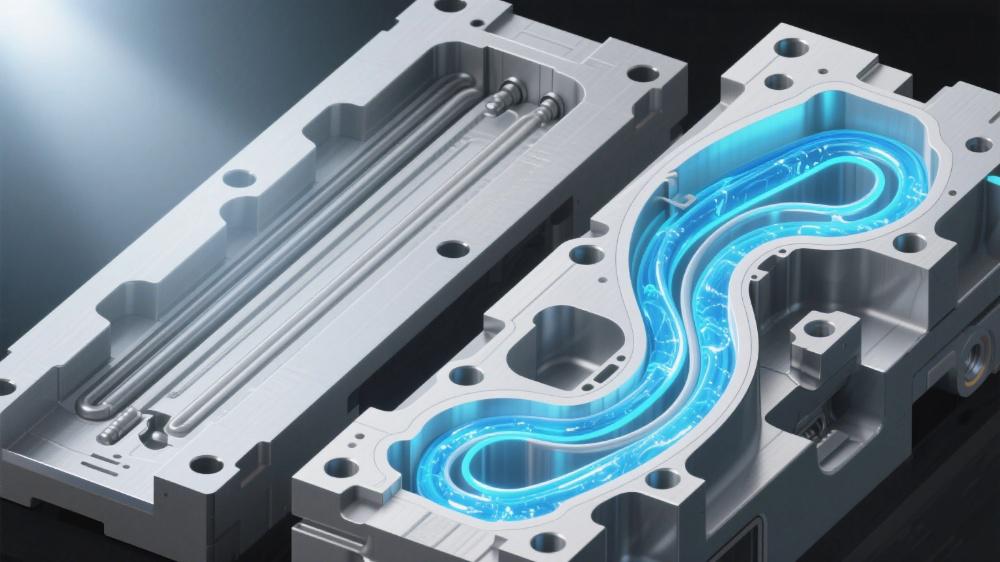

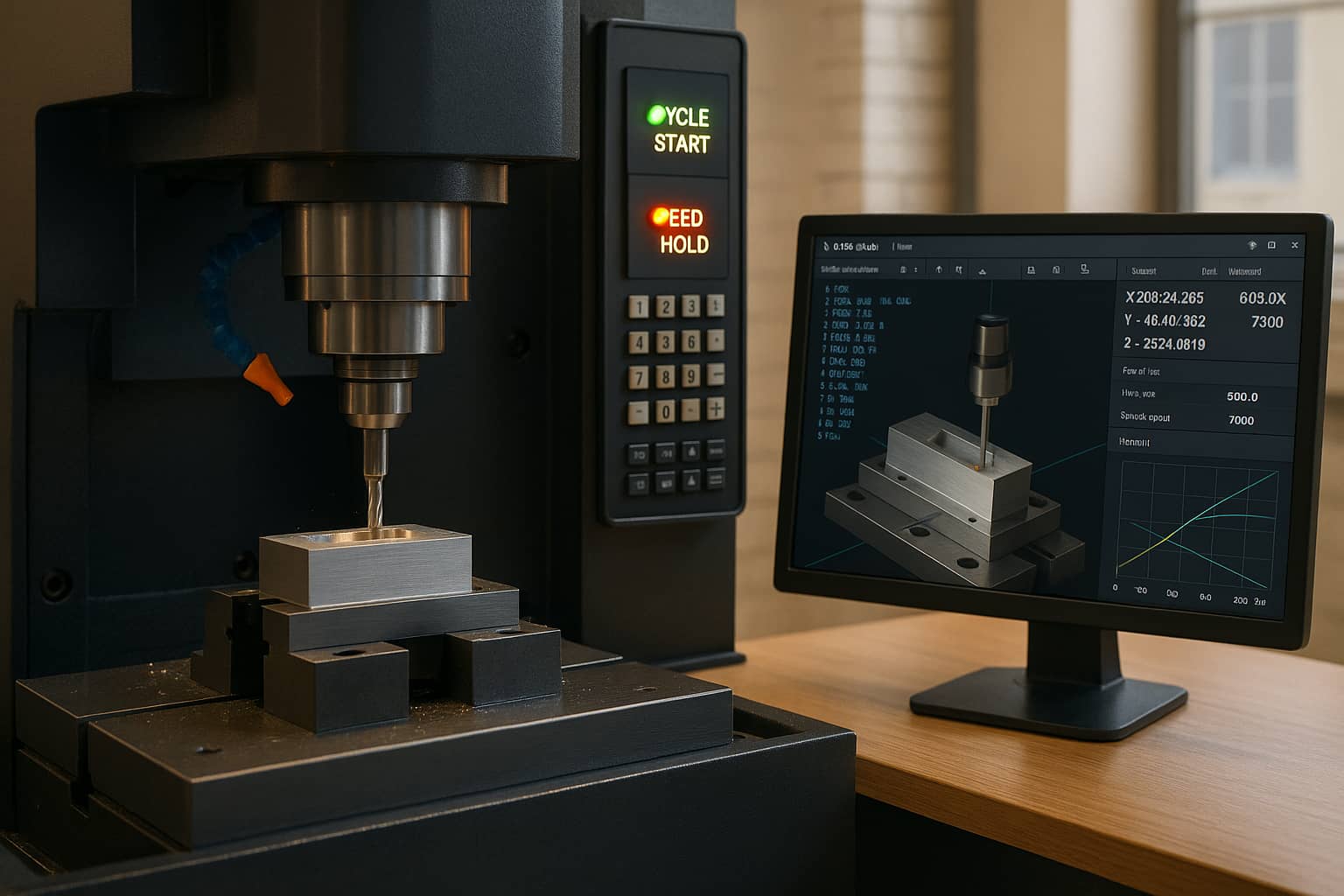
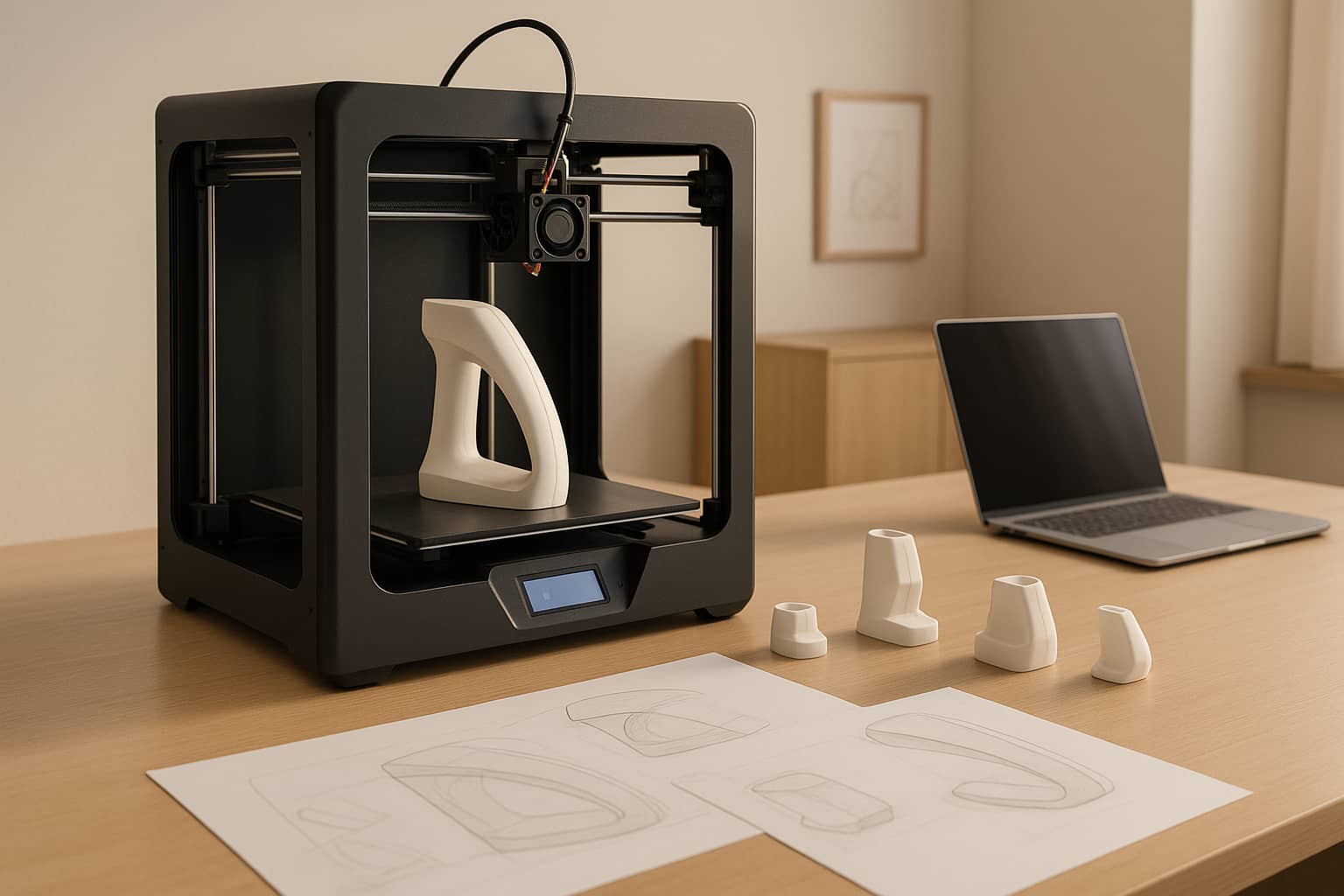
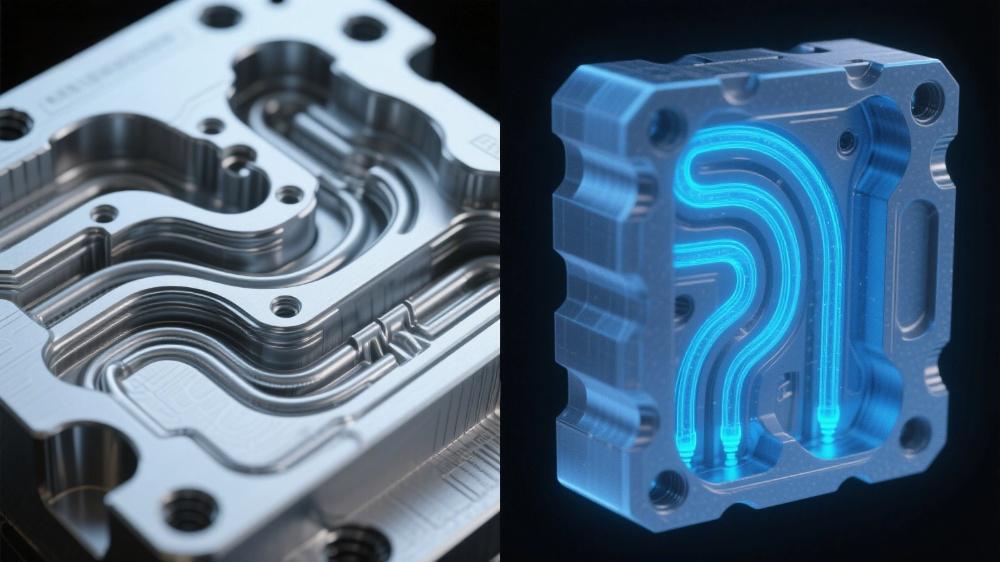
Conformal cooling refers to the design of mold cooling channels that precisely follow the shape of the casting part. Unlike traditional cooling systems—limited to straight or simple drilled channels by conventional machining (e.g., CNC drilling)—conformal channels deliver uniform heat distribution across every surface of the mold. Additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, is the enabler of this innovation.
Advanced AM technologies like laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and direct energy deposition (DED) allow manufacturers to create die casting molds with intricate, custom-tailored cooling channels. These channels can navigate around complex part geometries—including thin walls, undercuts, and internal features—that were previously impossible to cool evenly. For high-pressure die casting, this translates to transformative benefits: industry data shows AM-enabled conformal cooling can reduce HPDC cycle times by 20% to 40%, while cutting scrap rates (due to defects) by up to 35%.
Today’s manufacturing landscape demands three core priorities: faster time-to-market, higher part quality, and greater sustainability. Additive-manufacturing-enabled conformal cooling HPDC addresses all three, making it a cornerstone of Industry 4.0 initiatives:
The versatility of additive-manufacturing-enabled conformal cooling HPDC makes it applicable to a wide range of sectors, with tangible results:
Automotive Industry: EV manufacturers rely on HPDC for producing large, complex components like battery enclosures and e-motor housings. Conformal cooling ensures these parts cool evenly, preventing warping that could compromise battery safety or motor performance. For example, a leading EV maker recently reported a 30% reduction in cycle time for battery housing production after adopting the technology.
Medical Devices: Precision is non-negotiable in medical manufacturing. Conformal cooling molds produce consistent, defect-free components for devices like surgical instrument handles and diagnostic equipment casings. These parts meet strict biocompatibility standards (e.g., ISO 13485) and require zero tolerance for porosity or dimensional variation.
Household Appliances: From dishwasher pump housings to HVAC compressor parts, AM-enabled conformal cooling HPDC speeds up production of everyday items while improving durability. For instance, a major appliance brand reduced scrap rates for aluminum compressor parts by 28% after switching to conformal cooling molds.
As additive manufacturing technologies become more accessible and cost-effective, the adoption of conformal cooling in HPDC will accelerate. Emerging innovations—such as multi-material AM molds (combining heat-resistant alloys with thermal conductors) and AI-driven cooling channel design (optimized via simulation software like MAGMASOFT)—promise even greater efficiency gains.
For manufacturers looking to stay competitive in a fast-evolving market, embracing additive-manufacturing-enabled conformal cooling high-pressure die casting is no longer an option—it’s a strategic necessity. This technology doesn’t just improve production processes; it enables the creation of better, more innovative products that meet the demands of today’s consumers and industries.