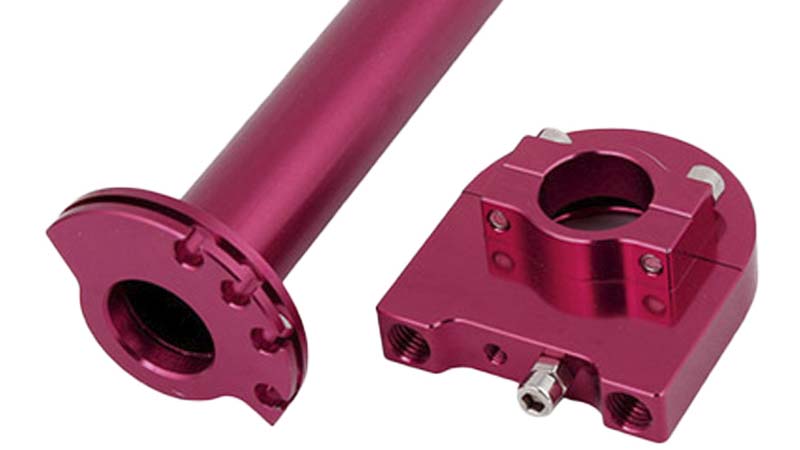
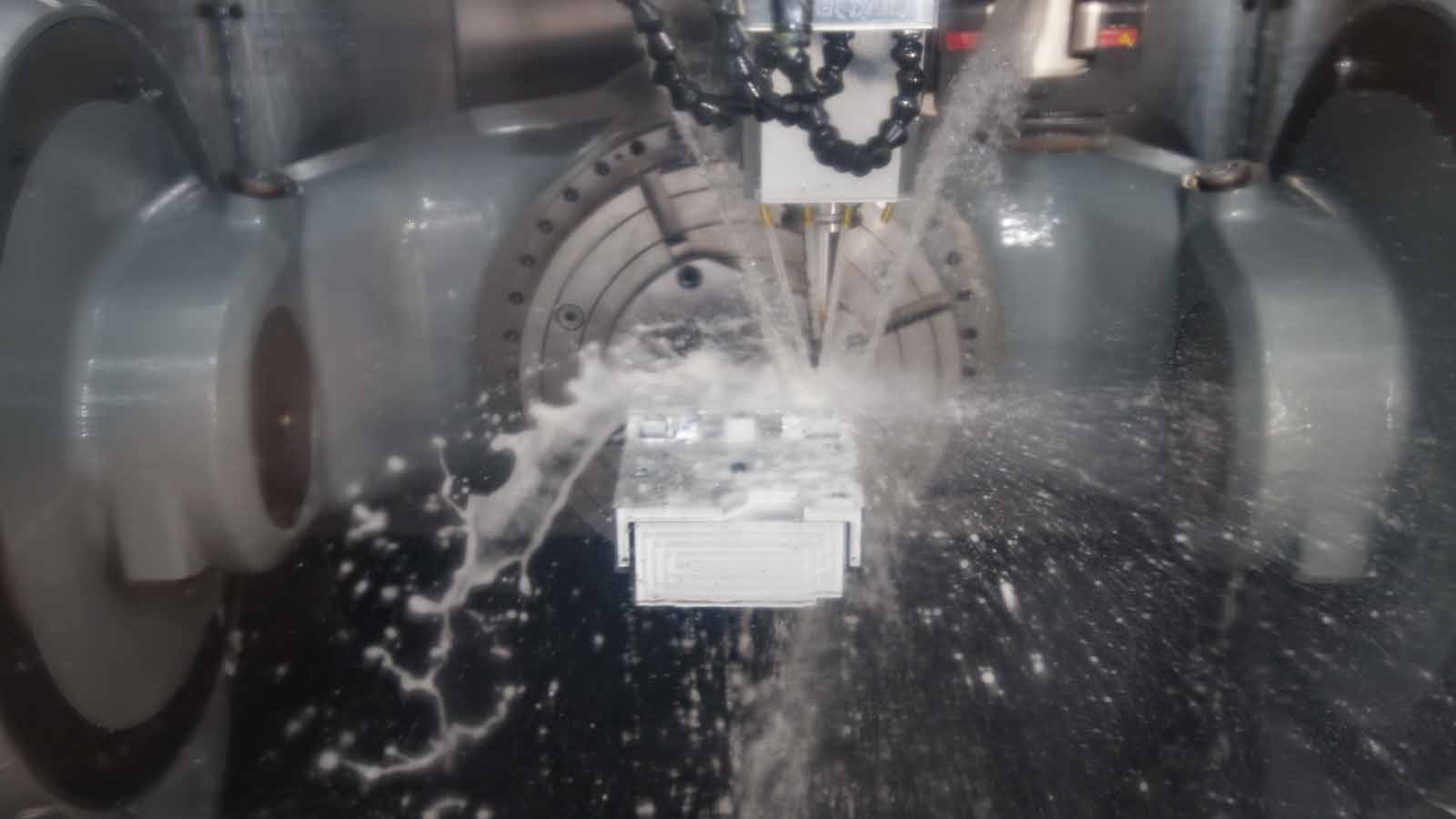
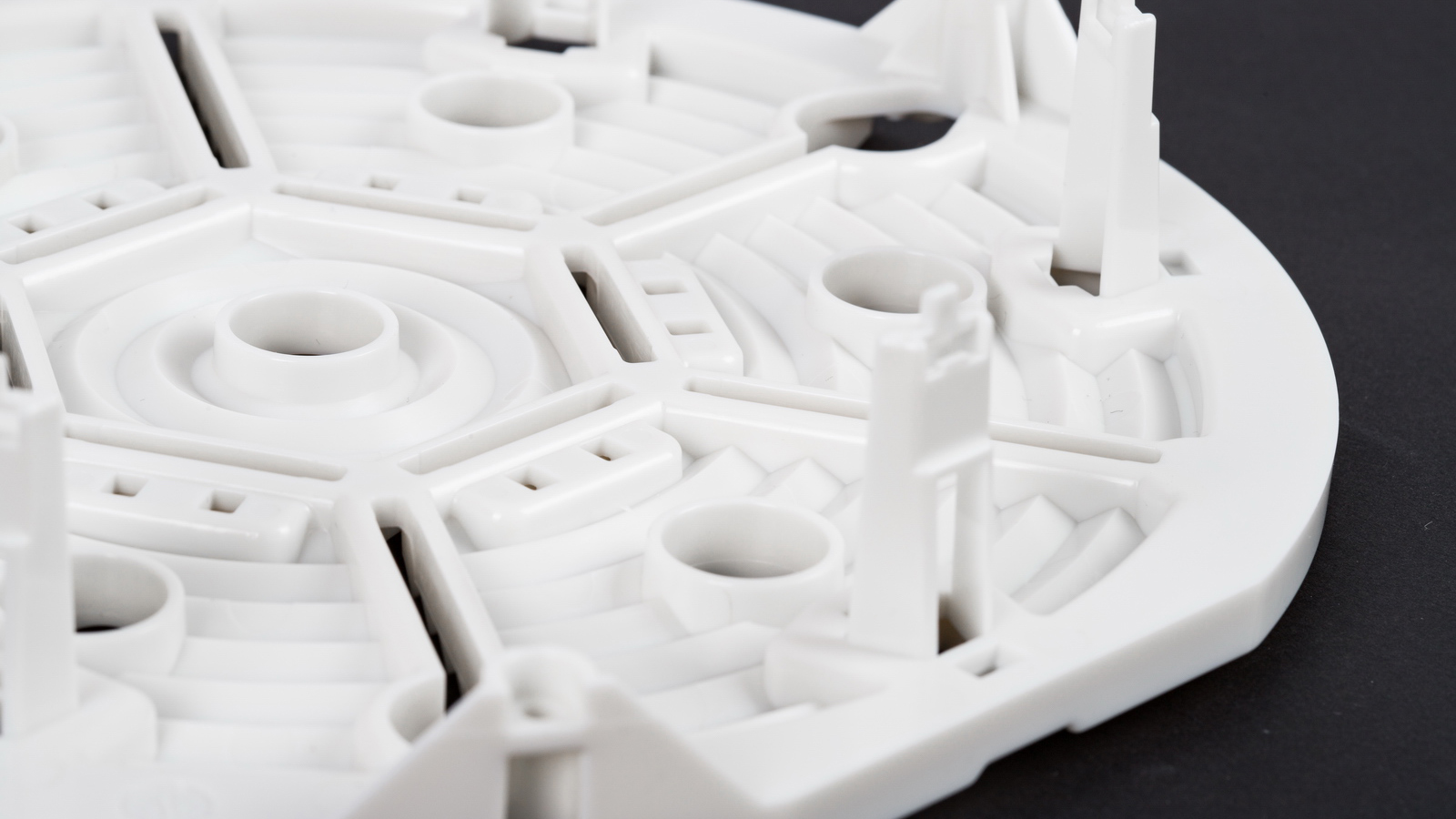
Mastars is a professional forging manufacturer with modern forging production line andstainless steel forging processing. Its products include valves, hardware parts, stainless steel and carbon steel. It has an annual production capacity of 800 tons of precision forged parts, and its products are sold all over the world.
Characteristics of forging
1. For the same part, forging can obtain fine grain structure and reduce defects such as pores in the part compared with other machining methods;
2. Continuous grain flow can be obtained to form mechanical fibrosis transition, so the material can obtain excellent mechanical properties such as maximum directional strength, impact resistance and fatigue resistance.
3. For the parts with complex shape, forging processing is more economical than mechanical processing, and is suitable for mass production, which can reduce the production cost.
4. Through the way of metal flow, forging has said that compared with other cutting processes, it can save more materials, reduce material loss and reduce production costs.

Forging category
1. Free forging
Free forging refers to the processing method of forging by using simple universal tools or directly applying external force to the blank between the upper and lower anvil of forging equipment to deform the blank and obtain the required geometry and internal quality; The forging produced by free forging method is called free forging; The basic processes of free forging include upsetting, drawing, punching, cutting, bending, torsion, dislocation and
forging.
(1) Lengthening
Drawing is also called extension. It is a forging process to reduce the cross-sectional area and increase the length of the blank; Drawing is often used for forging rod and shaft parts; There are two main methods of drawing length: drawing length on flat anvil and mandrel;
(2) Upsetting
Upsetting is a forging process in which the blank height is reduced and the cross-sectional area is increased. Upsetting process can effectively improve the blank structure and reduce the anisotropy of mechanical properties; Repeated upsetting and drawing can improve the morphology and distribution of carbides in high alloy tool steel;
(3) Punching
Punching is the forging process of punching through holes or non through holes on the blank; There are mainly two punching methods: double-sided punching method and single-sided punching method;
(4) Bend
Bending is a forging process in which a certain tool and die are used to complete the specified shape of the blank, which is called bending; There are two common bending methods: forging hammer pressing bending method and die bending method;
(5) Cut
Cutting refers to the forging process of dividing the blank into several parts or parts, or cutting part from the outside of the blank, or part from the inside;
(6) Dislocation
Stagger refers to the forging process in which one part of the blank is staggered for a certain distance from the other part, but the axis is still parallel; Commonly used for forging crankshaft parts; In case of dislocation, the blank shall be cut locally first, and then the impact force or pressure with equal size and opposite tangent method and perpendicular to the axis shall be applied on both sides of the incision to realize the dislocation of the blank.
(7) Forging joint
Forging joint is a forging process in which the blank is heated to high temperature in the furnace and then hammered quickly to combine the two in solid state; Forging methods include lap joint, butt joint, bite joint, etc; After forging, the joint strength can reach 70% ~ 80% of the strength of the connected material.
(8) Twist
Torsion is a forging process that rotates one part of the raw material relative to another part around its axis at a certain angle; This process is mostly used for forging multi crank crankshaft and correcting some forgings; When the torsion angle of small blank is small, the hammering method can be used.
Mastars Industries CO., LTD
www.mastars.com
Email: marketing@mastars.com
Tel: +86 755-88210690
Mobile: +86 181 0029 4997
Add: Building 6,Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China