
-

-
The world's largest automobile factory|automotive parts|moldMastars manufactures high-quality and highly accurate products for the automotive, electronics, medical and outdoor indu...
-

-
Material selection precautions of metal stamping die|rapid prototyping servicesMastars provides one-stop industrial manufacturing customization services from prototype to mass production. Rapid sheet...
-

-
The latest award-winning lightweight technology of andoto, Toyota and YanfengMastars provide Precision injection molding The industry covers a wide range of fields, including automobiles, motorcycl...
-

-
How Predictive Analytics Improves CNC MachiningPredictive analytics is transforming CNC machining by using data and machine learning to predict issues, optimise proces...
-

-
Full Guide for Selecting the Right CNC Material|MastarsYou must know that CNC technology is highly repeatable and accurate and offers a better manufacturing process for the pr...
-

-
Pepsi speeds up new bottle development with 3D printed molds|metal 3d printingPackaging design changes can be costly, especially in the bottled beverage industry. PepsiCo's R&D campus in New York St...
-

-
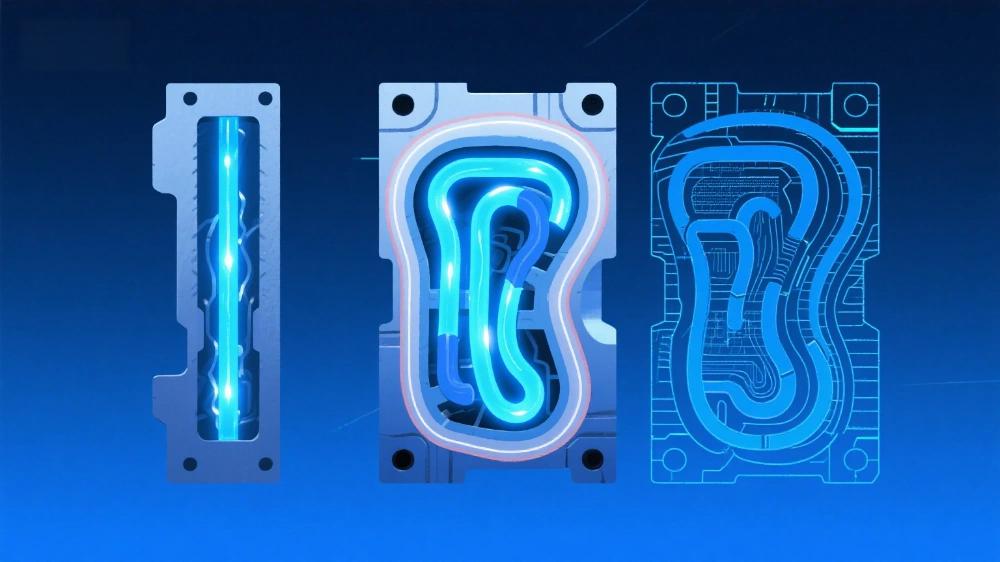
Additive-Manufacturing-Enabled Conformal Cooling High-Pressure Die CastingAdditive-Manufacturing-Enabled Conformal Cooling High-Pressure Die Casting High-pressure die casting (HPDC) has long bee...
-
-
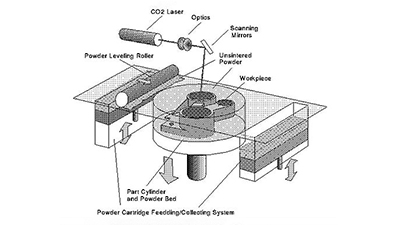
Mastars: Talk about common 3D printing technologies4Mastars' rapid prototyping service can provide various 3D printing prototyping services according to customers' needs, v...
-

-
Your Premier Guide to High-Quality Sheet Metal Prototyping ServicesYour Premier Guide to High-Quality Sheet Metal Prototyping Services | Mastars In the competitive world of manufacturing,...
Contact us
- Building 6 , Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City,Guangdong, China (518104)
- marketing@mastars.com
Key Terminologies in Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum Extrusion: Professional Terminology
Category 1: The Process & Press
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Aluminum Extrusion |
The manufacturing process where an aluminum
billet is forced through a die to create a long, continuous object with a
specific cross-sectional profile. |
|
Direct Extrusion |
The standard method where the billet is
pushed through a stationary die by a moving ram. |
|
Indirect Extrusion |
A less common method where the die moves
and pushes against a stationary billet. Reduces friction and required
pressure. |
|
Extrusion Press |
The main machine that performs the
extrusion, characterized by its tonnage (e.g., a
2,000-ton press). |
|
Container |
The thick-walled, high-strength steel
cylinder that holds the billet and withstands the immense pressure during
extrusion. |
|
Ram |
The large, hydraulically-driven piston that
applies force to the billet. |
|
Stem |
The part that connects the ram to the dummy
block. |
|
Dummy Block |
A reusable disc placed between the stem and
the billet. It seals the container and prevents aluminum from flowing
backward. |
Category 2: Materials & Inputs
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Billet |
A solid, cylindrical log of aluminum alloy
that is the starting material for extrusion. It is cast from molten aluminum. |
|
Alloy |
A specific blend of aluminum and other
elements (e.g., Magnesium, Silicon, Manganese) that determines the material's
properties. Common extrusion alloys are in the 6xxx series (e.g., 6061, 6063). |
|
Temper |
A designation indicating the mechanical
properties achieved through thermal and/or mechanical treatment. Key tempers
for extrusion include: |
|
Homogenization |
A pre-extrusion heat treatment of the
billet to create a uniform microstructure, improving extrudability and
surface quality. |
|
Extrusion Ratio |
The ratio of the cross-sectional area of
the container to the cross-sectional area of the extruded profile. A high
ratio indicates more severe deformation. |
Category 3: The Die & Tooling
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Die |
The tool steel disc with a shaped opening
that determines the profile's cross-section. It is the most critical and
custom part of the process. |
|
Die Stack |
The assembly consisting of the die
itself, the backer, and the bolster, which work
together to withstand extrusion pressure. |
|
Die Orifice / Bearing |
The final, shaped opening in the die. The
length of this opening (bearing length) is critical
for controlling metal flow. |
|
Solid Die |
A die used for producing solid
profiles (profiles with no enclosed voids). |
|
Hollow Die |
A die used for producing hollow
profiles (profiles with one or more enclosed voids). Requires a mandrel. |
|
Porthole Die |
A type of hollow die where the metal is
split into streams that flow around bridges (which hold
the mandrel) and are then welded back together inside the die chamber before
exiting. |
|
Bridge |
The part of a porthole die that supports
the mandrel. It creates weld
lines in the final profile. |
|
Mandrel |
The core component of a hollow die that
forms the inner surface of a hollow profile. |
|
Feeder Plate |
A plate used in conjunction with a die to
help control metal flow for complex shapes. |
Category 4: Profile Types & Geometry
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Profile |
The final, extruded product. Also called a shape or section. |
|
Solid Profile |
A profile with no enclosed voids. |
|
Hollow Profile |
A profile with one or more completely
enclosed voids (e.g., a tube or rectangular pipe). |
|
Semi-Hollow Profile |
A profile that partially encloses a void
but has a narrow, open gap that makes it less rigid than a true hollow. |
|
Cross-Section |
The two-dimensional shape of the profile
when cut perpendicular to its length. |
|
Tongue |
A narrow, protruding feature in the die
that forms a recess in the profile. Tongues are susceptible to deflection and
breakage. |
|
Wall Thickness |
The thickness of the material in the
profile. Maintaining uniform minimum wall thickness is a key design
constraint. |
|
Circle Size |
The smallest circle that can fully enclose
the profile's cross-section. This is a key parameter for pricing and press
capacity. |
Category 5: The Extrusion Cycle & Defects
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Butt |
The portion of the billet that remains in
the container after extrusion. It contains oxides and impurities and is
discarded for recycling. |
|
Breakthrough |
The moment when the aluminum first emerges
from the die orifice. |
|
Extrudate |
The hot, soft aluminum as it exits the die. |
|
Runout Table |
The conveyor system that supports the
extrudate as it exits the press. |
|
Quenching |
The rapid cooling of the extrudate using
air (air
quench) or water (water quench) to achieve the
desired temper. |
|
Stretching |
A post-extrusion operation where the
profiles are stretched (0.5-3%) to straighten them and align the grain
structure, improving strength. |
|
Die Lines |
Fine, longitudinal lines on the profile's
surface, caused by minor imperfections in the die bearing. |
|
Pick-Up |
Surface defects where small particles of
aluminum adhere to the die bearing, causing scratches on the profile. |
|
Weld Lines / Seam Welds |
Longitudinal lines in a hollow profile
where the metal streams were re-welded after flowing around the bridges in a
porthole die. A potential weak point if not done correctly. |
Category 6: Post-Extrusion & Finishing
|
Term |
Definition & Context |
|
Age Hardening (Artificial Aging) |
A heat-treatment process where extruded
profiles are heated for a specific time to increase their strength (achieving
T5 or T6 temper). |
|
Anodizing |
An electrochemical process that thickens
the natural oxide layer on the aluminum, providing superior corrosion
resistance and allowing for coloring. |
|
Powder Coating |
A dry finishing process where
electrostatically charged powder is applied to the profile and then cured
under heat to form a durable, colored coating. |
|
Fabrication |
Secondary operations performed on extruded
profiles, such as cutting, drilling, milling, tapping, and welding. |
|
Mitering |
Cutting profiles at an angle for assembly
at corners. |
【Editor】:Mastarsall rights reserved:https://www.mastars.comPlease indicate the source






