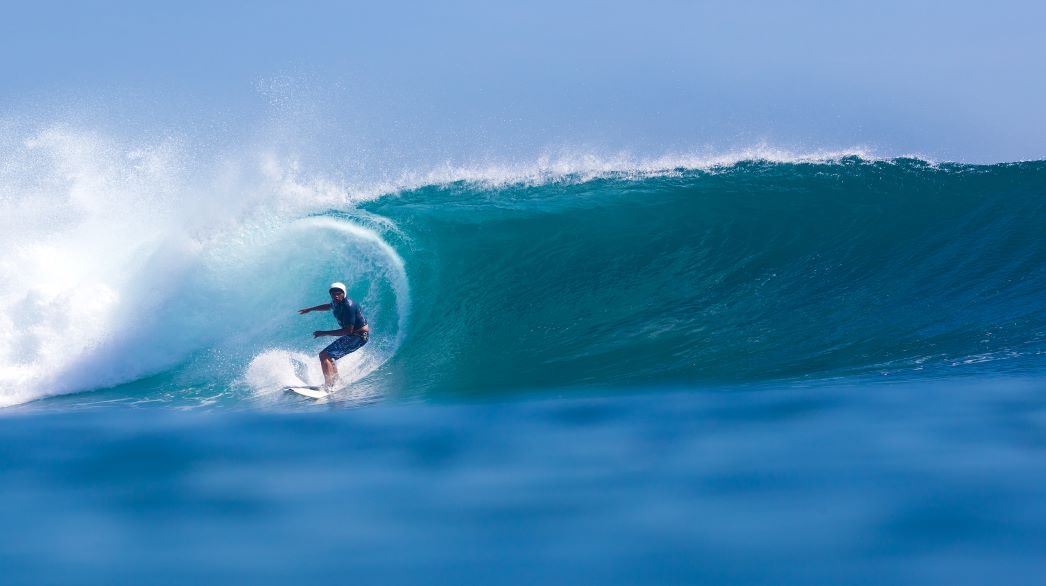
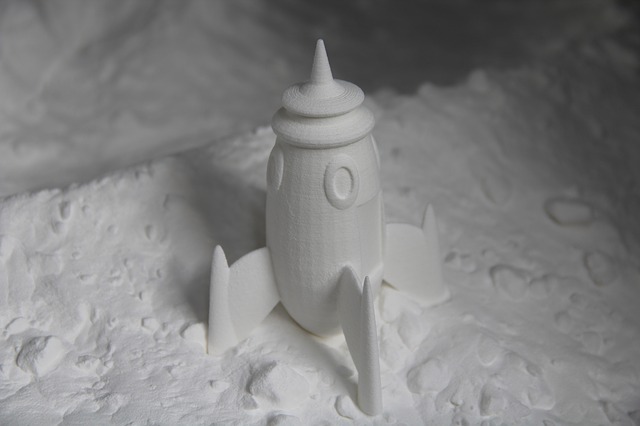
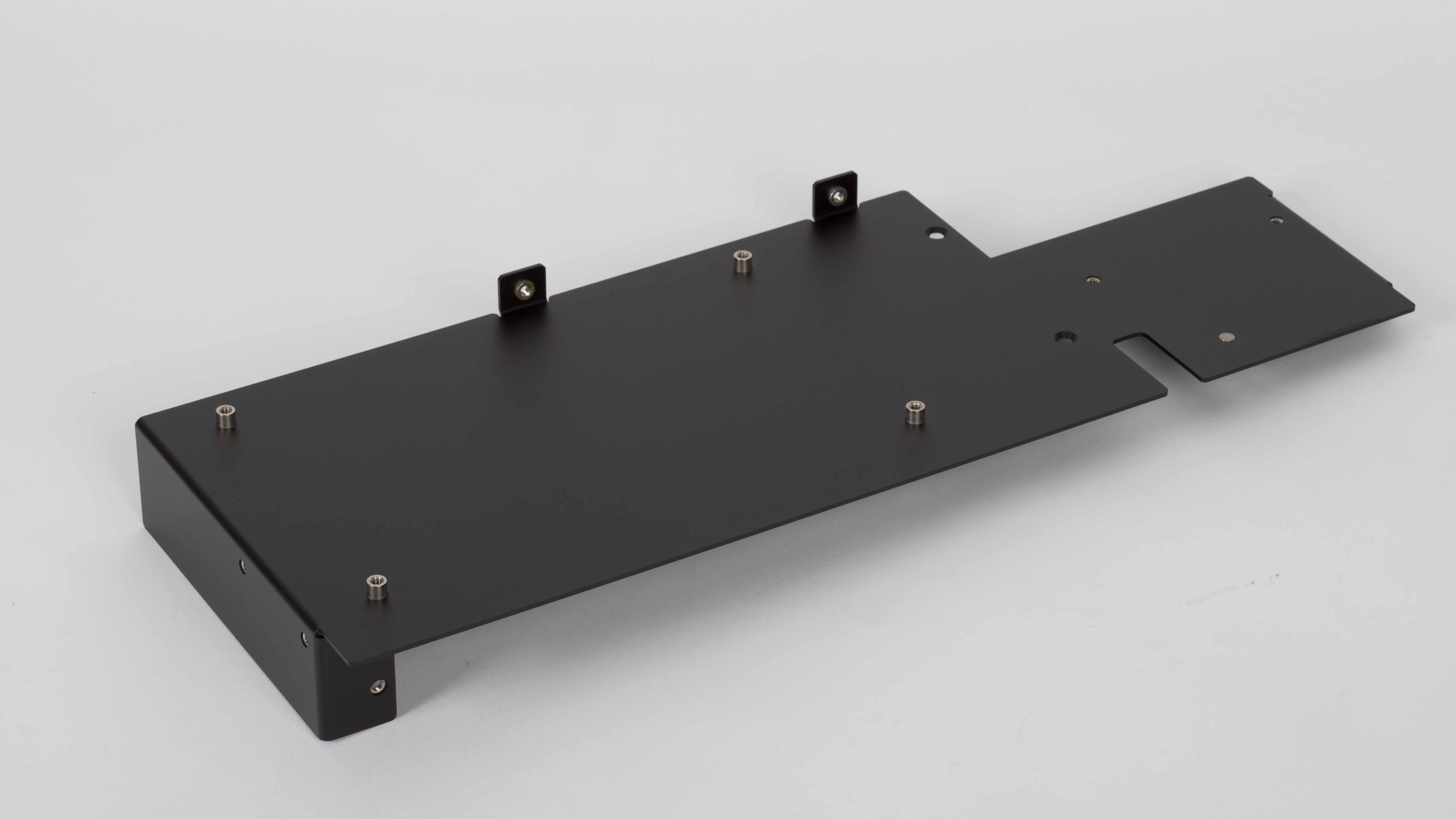
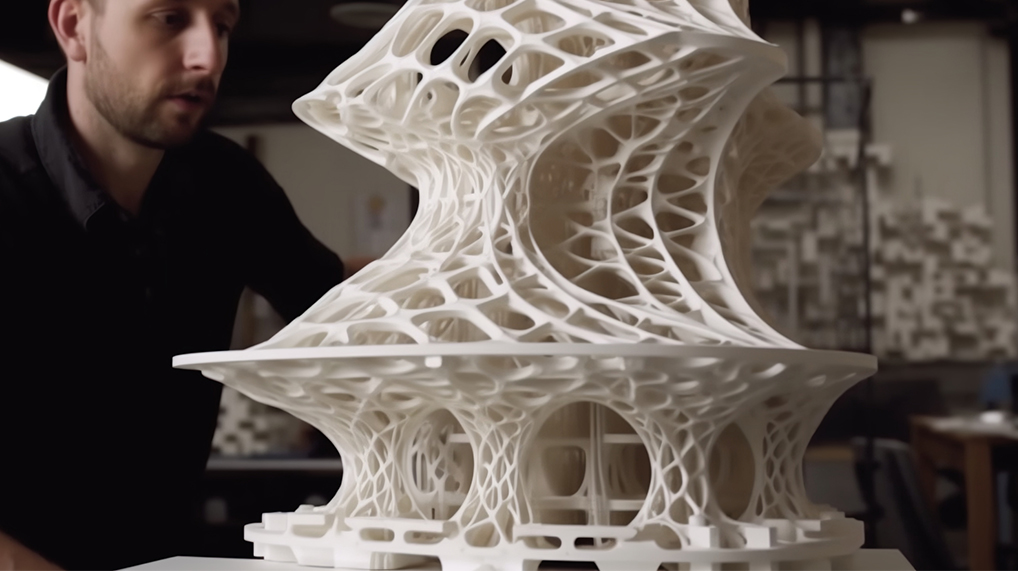
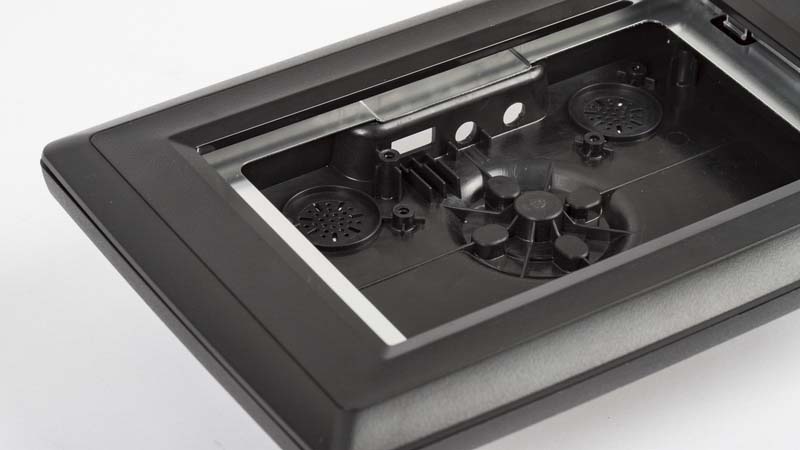
The prototype is one or several functional templates made according to the product appearance drawing or structure drawing without opening the mold to check the rationality of appearance or structure. With the progress of science and technology and the rapid development of CAD and CAM technology, it provides better technical support for prototype manufacturing, making the accurate manufacturing of prototype possible. Mastars is a professional company specializing in prototyping, rapid prototyping, CNC parts processing, 3D printing, laser molding, manufacturing, mass production and mold reproduction, etc., to provide customers with comprehensive and professional product manufacturing needs.So what are the classifications of prototypes and the comparison of different categories? Let's have a look.
Classification of prototypes
1. Prototypes can be divided into:
(1) Manual prototype: its main workload is completed by hand.
(2)
CNC prototype: its main workload is completed by NC machine tools. According to different equipment, NC prototype can be divided into:
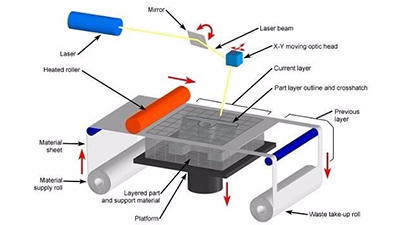
RP prototype: it is mainly produced by laser rapid prototyping technology.
CNC prototype: it is mainly the prototype produced by machining center.
2. The prototype can be divided into:
(1) Plastic prototype: its raw material is plastic, mainly the prototype of some plastic products, such as TV, display, telephone and so on.
(2) Metal prototype: its raw materials are aluminum magnesium alloy and other metal materials, mainly the prototype of some high-end products. Such as notebook computer, advanced single player, MP3 player, CD player, etc.

Comparison between RP prototype and CNC prototype
1. RP prototype should be expressed in its rapidity, but it is mainly formed by stacking technology. Therefore, RP prototype is generally relatively rough and has certain requirements for the wall thickness of the product. For example, if the wall thickness is too thin, it can not be produced. The advantage of CNC prototype is that it can accurately reflect the information expressed in the drawing, and the surface quality of CNC prototype is high. Especially after surface spraying and silk screen printing, it is even brighter than the products produced after opening the mold. Therefore, CNC prototype manufacturing has increasingly become the mainstream of prototype manufacturing industry.
2. The use of
rapid prototyping in the field of mechanical manufacturing is widely used in the field of mechanical manufacturing because of the characteristics of RP technology. It is mostly used to make single piece and small batch metal parts. The cost of RP is generally less than 50, because the cost of RP is generally less than 50. The use of rapid prototyping skills in mold making can be divided into direct mold making and direct mold making. Direct mold making refers to the direct accumulation of RP skills to make molds. Direct mold making refers to making rapid prototyping parts first, and then copying the required molds from the parts.
There are many categories of prototypes. Although CNC prototypes occupy the mainstream position in the prototype manufacturing industry, prototypes of other processing methods can not be ignored and are always applicable. With the continuous progress of science and technology, prototype processing methods with wider application, higher efficiency and higher precision are bound to appear.
Mastars Industries CO., LTD
www.mastars.com
Email: marketing@mastars.com
Tel: +86 755-88210690
Mobile: +86 181 0029 4997
Add: Building 6,Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China