









What Is Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printing is a manufacturing process that creates complex parts. Healthcare, automotive, and aerospace industries use 3D printing metal to get products fast without hurting their budget. They will have to spend more on the conventional manufacturing process. Also, metal 3D printing has witnessed many improvements to create better solutions for different industries. Now, it is the most popular method in the manufacturing process. In addition to this, metal 3D technologies can create prototypes and even the finished product.For example, we offer rapid prototyping services.

3D printing service does not focus on a single technology. Yes, the process involves different types of technologies. All the technologies will have some specific requirements. Yes, the term metal 3D printing applies to many technology families. It is a broad concept and covers many technologies and processes. In a simpler term, metal 3D printing produces metal products layer by layer with some different methods. The process involves sintering, melting, and finally welding. All these come together in the metal 3D printing process.Nowadays, with the rapid development of science and technology, metal 3D printing technology with the advantages of short-term manufacturing, on-demand manufacturing and rapid prototyping is making many impossible.
At present, there are five mainstream Metal 3D printing technologies in the market: laser selective sintering (SLS), nano particle jet metal forming (npj), laser selective melting (SLM), laser near net forming (lens) and electron beam selective melting (EBSM). Next, let's introduce the basic working principles of these five metal 3D printing technologies.
SLS laser selective sintering
Working principle: lay a layer of powder material on the worktable in advance. Under the control of the computer, the laser will sinter the solid part of the powder according to the interface contour information, and then continuously circulate and stack it layer by layer.
SLS method uses infrared laser as energy, and most of the molding materials used are powder materials. During processing, first preheat the powder to a temperature slightly lower than its melting point, and then pave the powder under the action of a leveling stick; The laser beam is selectively sintered according to the layered section information under the control of the computer. After one layer is completed, the next layer is sintered. In this way, it is repeated and stacked layer by layer until the three-dimensional part is formed. Finally, the unsintered powder is recovered into the powder cylinder and the molded part is taken out.
Because the molding method has the characteristics of simple manufacturing process, high flexibility, wide range of material selection, low material price, low cost, high material utilization rate and fast molding speed, it is mainly used in the casting industry and can be used to directly make rapid molds.
Npj nanoparticle spray metal forming
Working principle: first put the metal into the 3D printer in the form of liquid, and spray it with liquid containing metal nanoparticles during printing. Then, the excess liquid is evaporated by heating, leaving the metal part. Finally, the molding is completed by low-temperature sintering.
The forming method can use an ordinary inkjet print head as a tool, and the supporting structure can be melted and removed through special technology without the help of any external force. Because it is removed by melting, it can be added infinitely in theory, giving designers greater freedom. In addition to metal materials, its breakthrough in ceramic technology has extended its application to dental, medical and specific industrial fields.
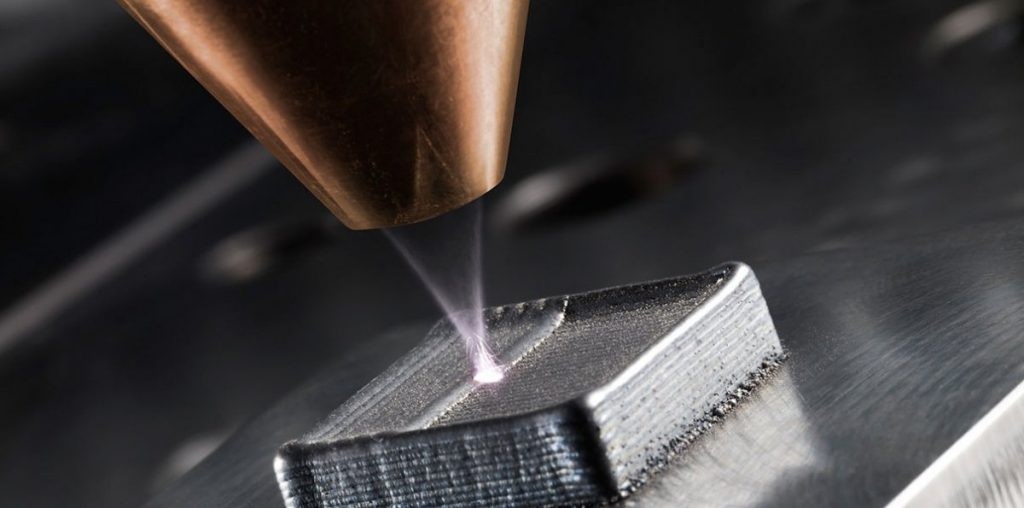
SLM laser selective melting
Working principle: use high-energy laser beam to melt the metal alloy powder on the two-dimensional section after slicing the three-dimensional model, and print metal parts with arbitrary complex structure and nearly 100% density layer by layer from bottom to top.
SLM technology mainly uses CAD three-dimensional software to design three-dimensional models and export them into file formats that can be recognized by slicing software; Slice the 3D model, add support and layer processing, and get the profile data of the 3D model; The scanning path of the contour data is processed by the path planning software, and the data after the path planning is imported into the SLM equipment. According to the scanning path of each layer of contour, the industrial computer controls the laser beam selection to melt the metal alloy powder layer by layer, and stack it layer by layer into a dense three-dimensional metal part entity.
The advantage of SLM technology lies in its high utilization rate of materials, high dimensional accuracy of metal parts, and free design. Its limitation lies in the high cost of equipment components, the inability to realize the mass production and processing of products, and the non-uniform standard of metal alloy powder. Therefore, SLM is mainly used in aerospace, biomedicine and other fields. It is suitable for the manufacturing of precious and difficult to process metal parts such as titanium alloy and nickel alloy.
Lens laser near net forming
Working principle: the computer slices the three-dimensional CAD model of the part, obtains the two-dimensional plane contour data of the part, and converts the contour data into the motion track of the NC worktable. At the same time, the metal powder is sent into the laser focusing area at a certain powder supply speed to melt and solidify rapidly. Through the superposition of points, lines and surfaces, the three-dimensional near net metal parts are finally formed.
Lens can realize the dieless manufacturing of metal parts. The formed parts have dense structure, obvious rapid melting characteristics and high mechanical properties. It can also realize the manufacturing of heterogeneous and gradient material parts and the processing of high-strength metal parts such as titanium alloy.
Ebdm electron beam selective melting
Working principle: firstly, slice and layer the 3D CAD model of the part, and input the obtained discrete data into the forming system. Preheating treatment is carried out in the forming system, and then the electron beam will melt the powder pre laid on the workbench according to the part CAD data. After the processing of one layer is completed, the workbench will drop one layer thick, and then the powder laying and melting of the next layer will be carried out. At the same time, the new melting layer will be fused with the previous layer. This is repeated, stacked layer by layer, and directly formed to produce three-dimensional parts.
Ebdm technology has the advantages of fast processing speed, high energy utilization rate, low vacuum pollution, low component residual stress and no reflection. It is especially suitable for the direct molding of active, refractory and brittle metal materials. It has broad prospects in the fields of aerospace, biomedical automobile molds and so on.
Mastars Industries CO., LTD
www.mastars.com
Email: marketing@mastars.com
Tel: +86 755-88210689
Fax: +86 755-8821 0685
Add: Building 6,Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China
Contents:
3D printing