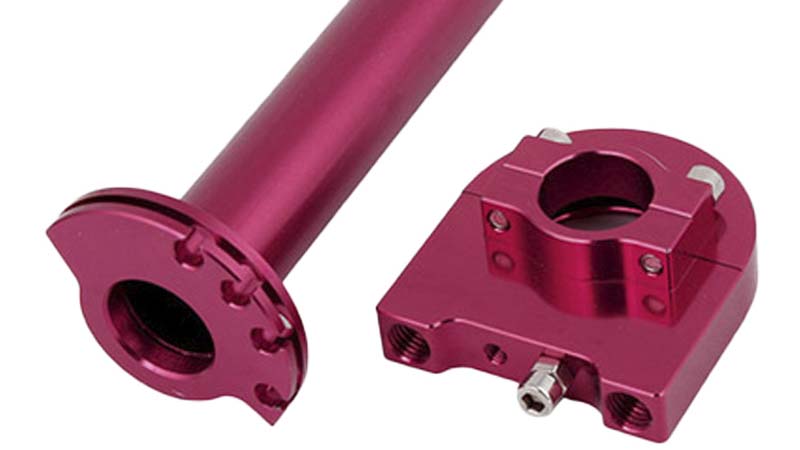
The purpose of surface treatment is to meet the requirements of corrosion resistance, wear resistance, decoration or other special functions of products, which is also called secondary processing.

Micro arc oxidation, also known as micro plasma oxidation, is the combination of electrolyte and corresponding electrical parameters. On the surface of aluminum, magnesium, titanium and their alloys, ceramic films dominated by matrix metal oxides are grown by the action of instantaneous high temperature and high pressure generated by arc discharge.
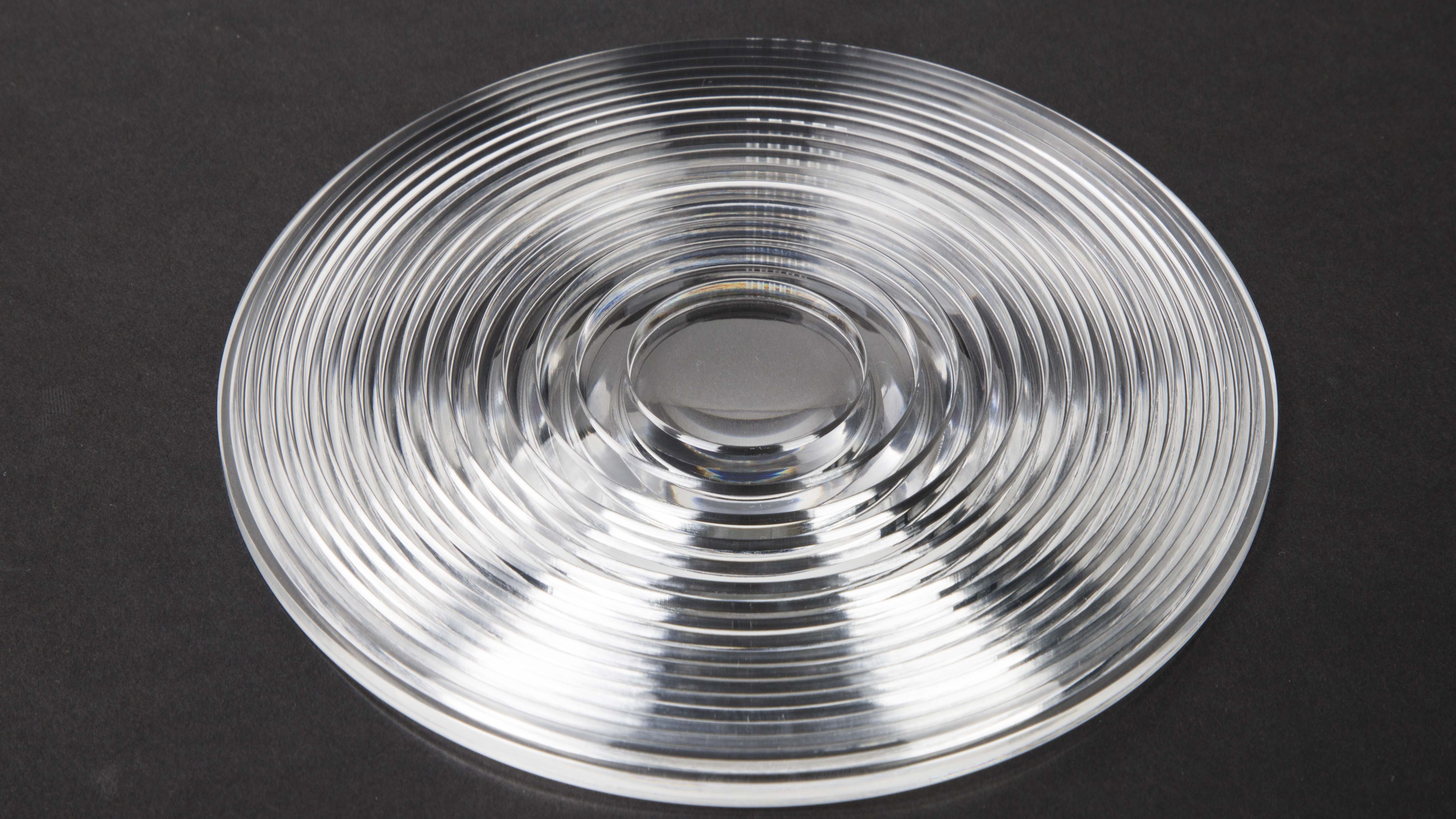
Metal wire drawing is a surface treatment method that forms lines on the surface of workpieces by grinding products to achieve decorative effects.
Blue burning is to fill the whole carcass with colored glaze, and then bake it in a blast furnace with a furnace temperature of about 800 ℃. The colored glaze melts from sand like solid into liquid, and becomes a gorgeous colored glaze fixed on the carcass after cooling. At this time, the colored glaze is lower than the height of copper wire, so it has to be filled with colored glaze again, and then sintered, generally four or five times continuously, until the pattern is filled to be level with the wire pinching pattern.
Shot peening is a cold working process that uses shot particles to bombard the surface of the workpiece and implant residual compressive stress to improve the fatigue strength of the workpiece.
Sand blasting is a process of cleaning and roughening the surface of the substrate by using the impact of high-speed sand flow, that is, using compressed air as the power to form a high-speed jet beam to spray the spray material (copper ore, quartz sand, carborundum, iron sand, Hainan sand) to the workpiece surface to be treated at high speed, so as to change the appearance or shape of the outer surface of the workpiece surface.
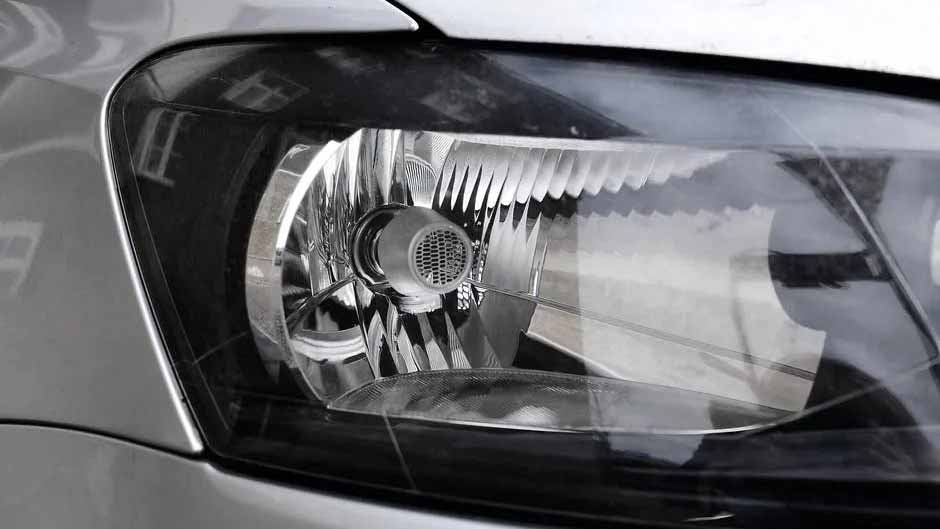
Etching is the technology of removing materials by chemical reaction or physical impact. Generally, the term "etching" is also called photochemical etching, which refers to the removal of the protective film of the area to be etched after exposure plate making and development, and the contact with chemical solution during etching, so as to achieve the effect of dissolution and corrosion, and form the effect of concave convex or hollow molding.