Mastars is a plastic and metal parts manufacturer, producing and selling: stamping, plastic moulds, stamping parts, plastic parts; providing rapid CNC machining, plastic molds, for electronics, electrical appliances, automotive, office supplies, cosmetics, medical equipment, 3C industries.
When companies implement additive manufacturing for existing products, one of the primary challenges they must face has to do with materials. While the variety and number of materials suitable for additive manufacturing is growing, there is no guarantee that they will be equivalent to traditional injection molding resins, casting alloys or machined materials are equivalent.
At the same time, the shift from traditional processes to additive manufacturing offers the opportunity to rethink materials. For example, titanium is a material that is difficult to machine, but easy to print. Parts that were previously milled from steel may be easier to 3D print with titanium via powder bed fusion. Or, machined parts that don't need metal at all can be made lighter and easier with 3D printed plastic.
The design benefits of additive manufacturing also play an important role in material selection.
3D printing allows multiple parts of a component to be combined, often into just one part. This merging simplifies production and labor, but it also reduces the use of fasteners and the amount of material used. For example, assemblies that weld together tool steel and aluminum can be replaced entirely with nylon parts. The resulting product may be lighter and easier to manufacture, but it is also easier to recycle because it does not need to be broken down into separate materials first.

In addition to these benefits, 3D printing offers some unique material opportunities. A growing number of manufacturers are offering plastics for 3D printing that are made from recycled resources as well as bio-based polymers such as PLA made from renewable plant sources.
Composites reinforced with recycled carbon fiber and biodegradable materials such as wood fiber are also being developed. In metals, there are fewer options for recycled materials, but technology and materials suppliers are coming up with new ways to mechanically recycle metals into entirely new combinations of
gold, using processing chips for 3D printing, and atomizing scrap in small batches for use as metal powder.
Optimization supports more efficient products
Design for manufacturing is a best practice for product development, but additive manufacturing engineers are focused on a much broader range. Additive manufacturing design considers more than just the manufacturing steps of the part in question; it must also consider materials (since material properties are set primarily during the printing process), build parameters, part orientation, support structures, and any necessary post-processing. Additive manufacturing greatly expands the scope of design and requires engineers to follow the original design intent through a longer chain. This is a change in mindset, as well as an organizational and technical
technology change.
While additive manufacturing makes the design phase more complex, it also opens up new possibilities. Advanced software tools for topology optimization, derivative design, and simulation help engineers get better designs that can only be produced through additive processes. While the first use of 3D printing was as a
rapid prototyping tool, finite element analysis and print simulation tools, are pointing to sustainable manufacturing that relies on digital prototyping.
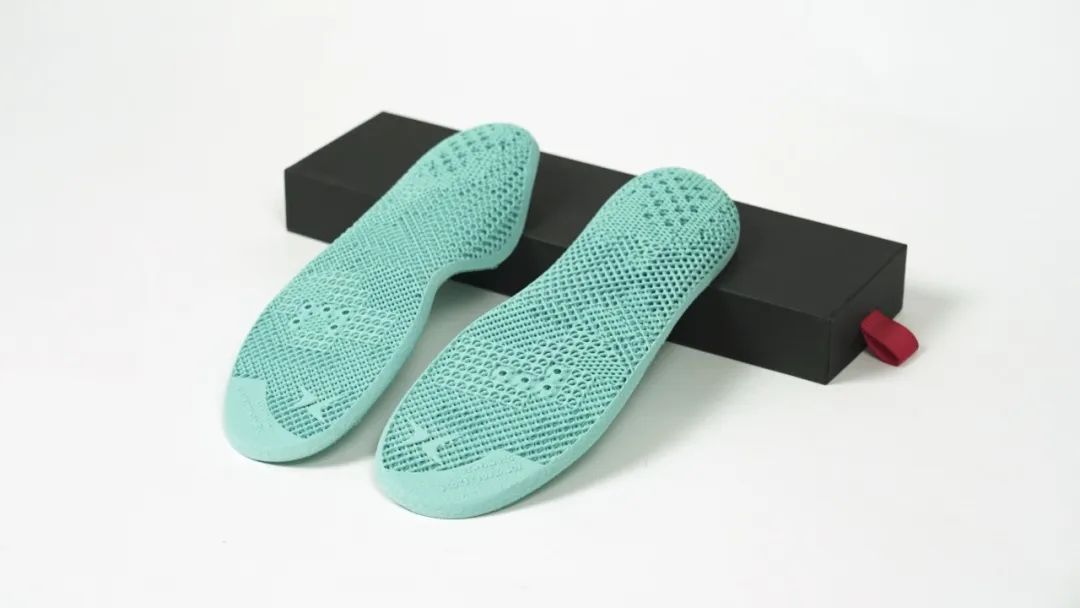
With 3D printing and software-driven design, materials can be applied exactly where they are needed and manipulated through features such as lattices to give different properties in different areas. The concept of "digital foam" relies on this capability. For example, an entire insole can be made from just one material, but printed using different lattice geometries to provide cushioning in areas where certain properties are needed.
Electric cars and airplanes are made possible through additive manufacturing and design software to make lightweighting and performance optimization a reality. These lightweight components will contribute to longer battery life, longer flight distances and longer space travel. As new designs are realized through additive manufacturing, human activities such as travel and exploration will become more energy efficient and sustainable.
As parts or entire products are reinterpreted for additive manufacturing, additive design also offers the opportunity to reconsider what happens to parts at the end of their useful life. Decisions made during the design phase, such as the use of fasteners, interchangeable parts and material diversity, will affect how easy it is to remanufacture or break down a product for later recycling.