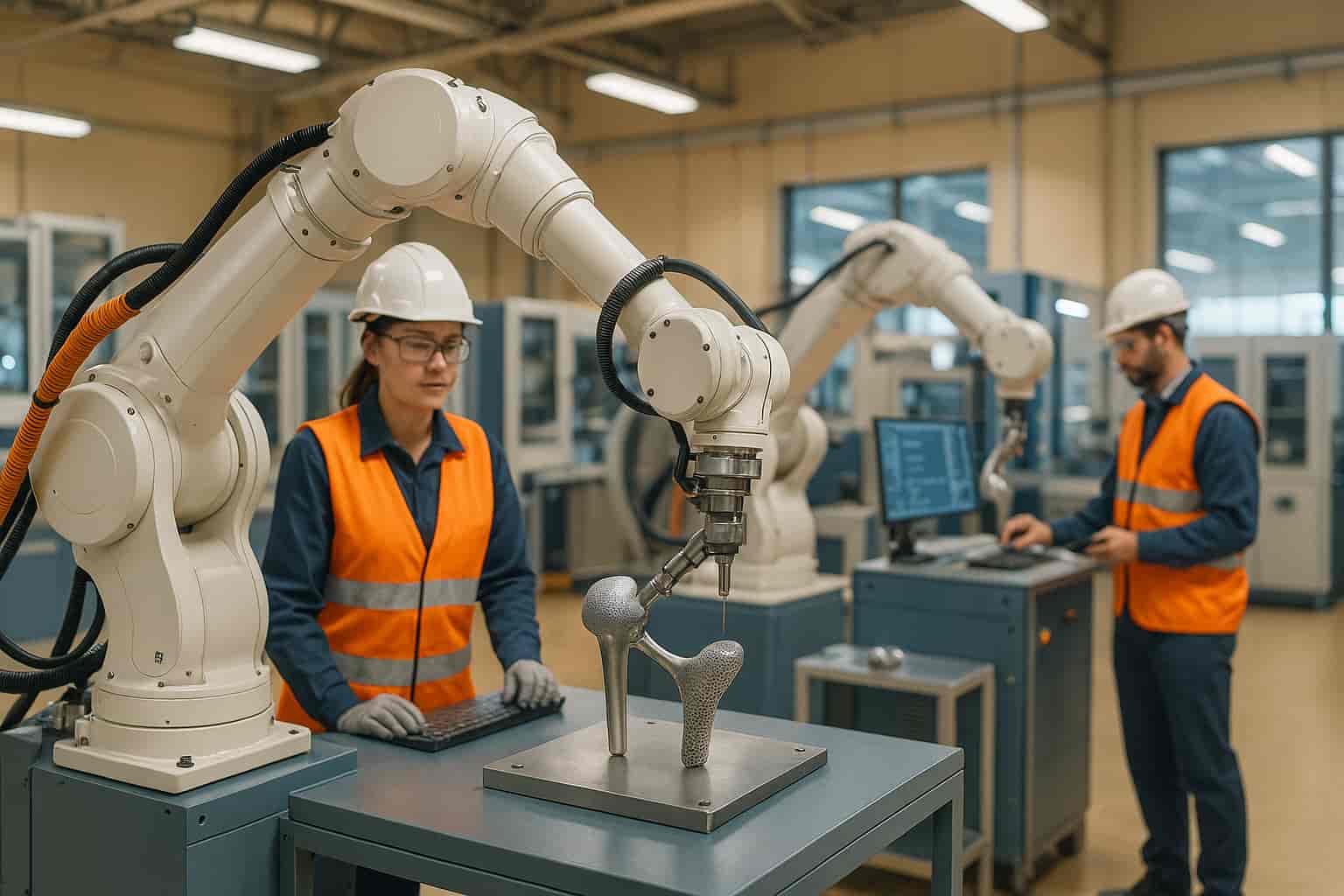
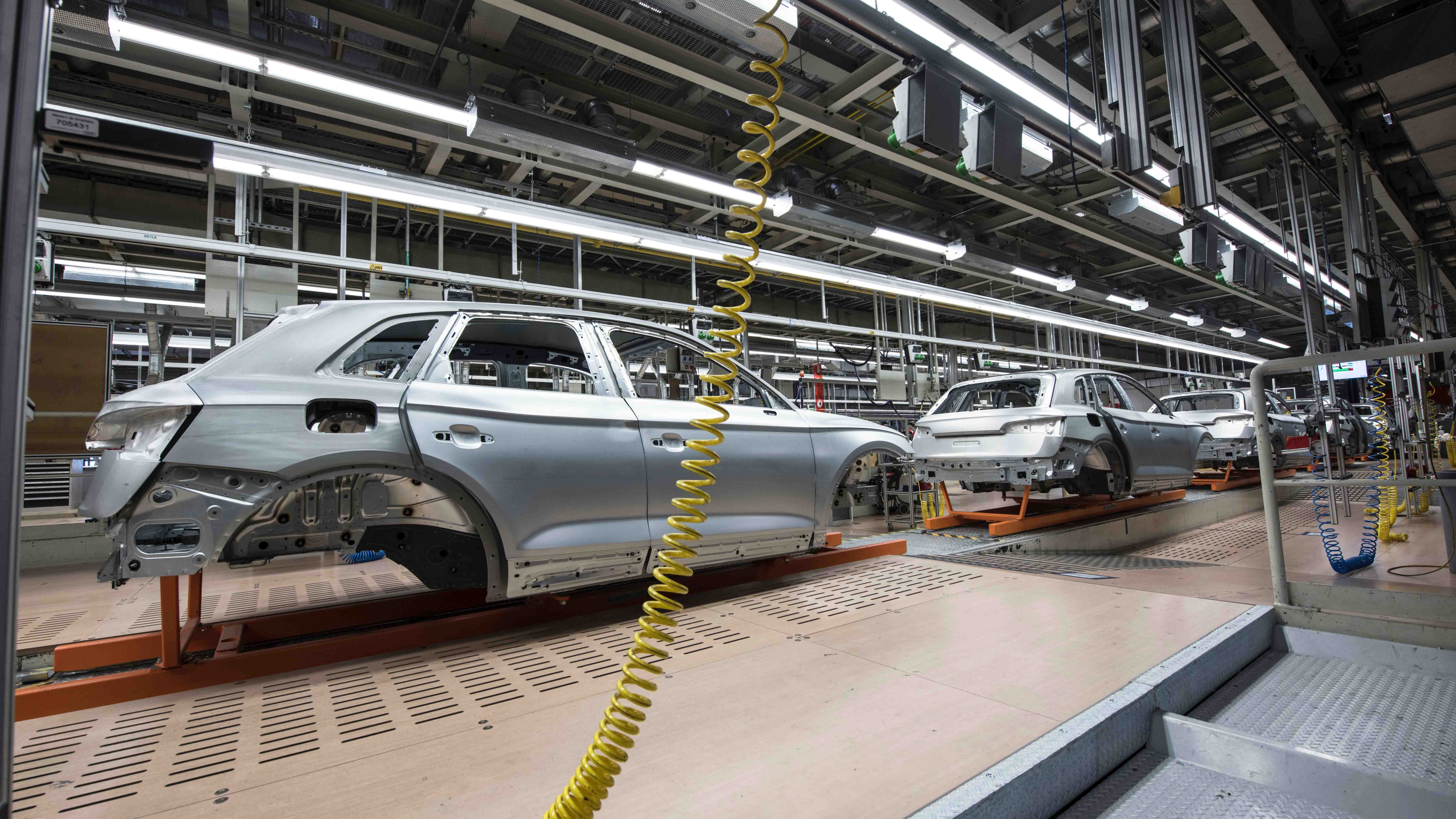
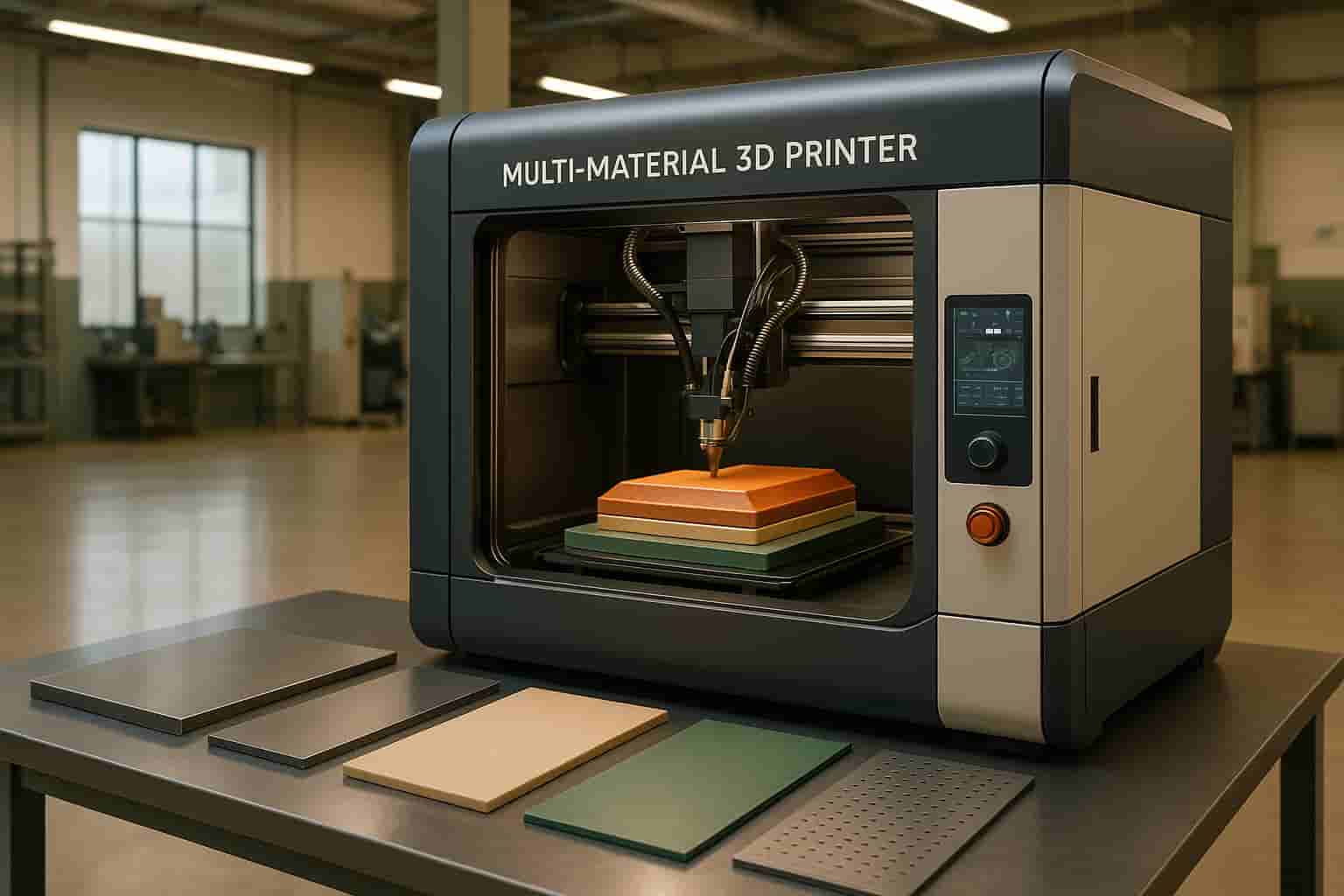
Mastars provides rapid parts production services for automotive, heavy industry, machinery, electronics, general machinery, etc. Including
rapid prototyping services, rapid cnc services,
sheet metal prototyping, etc.Additive manufacturing is a complex design that runs through CAD software with high accuracy and is used in a variety of industries and applications. Different manufacturing technologies each have their own characteristics, so what is the difference between additive manufacturing and other manufacturing methods?
01 Additive Manufacturing
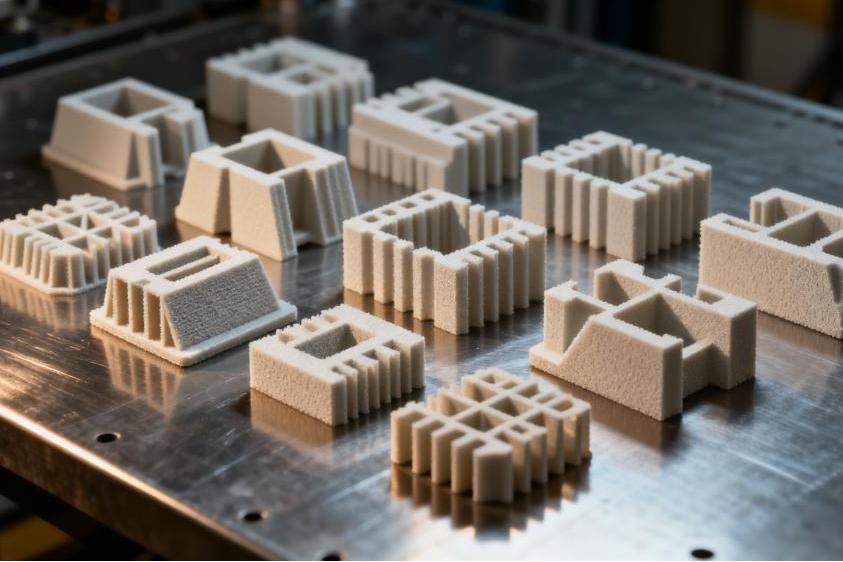
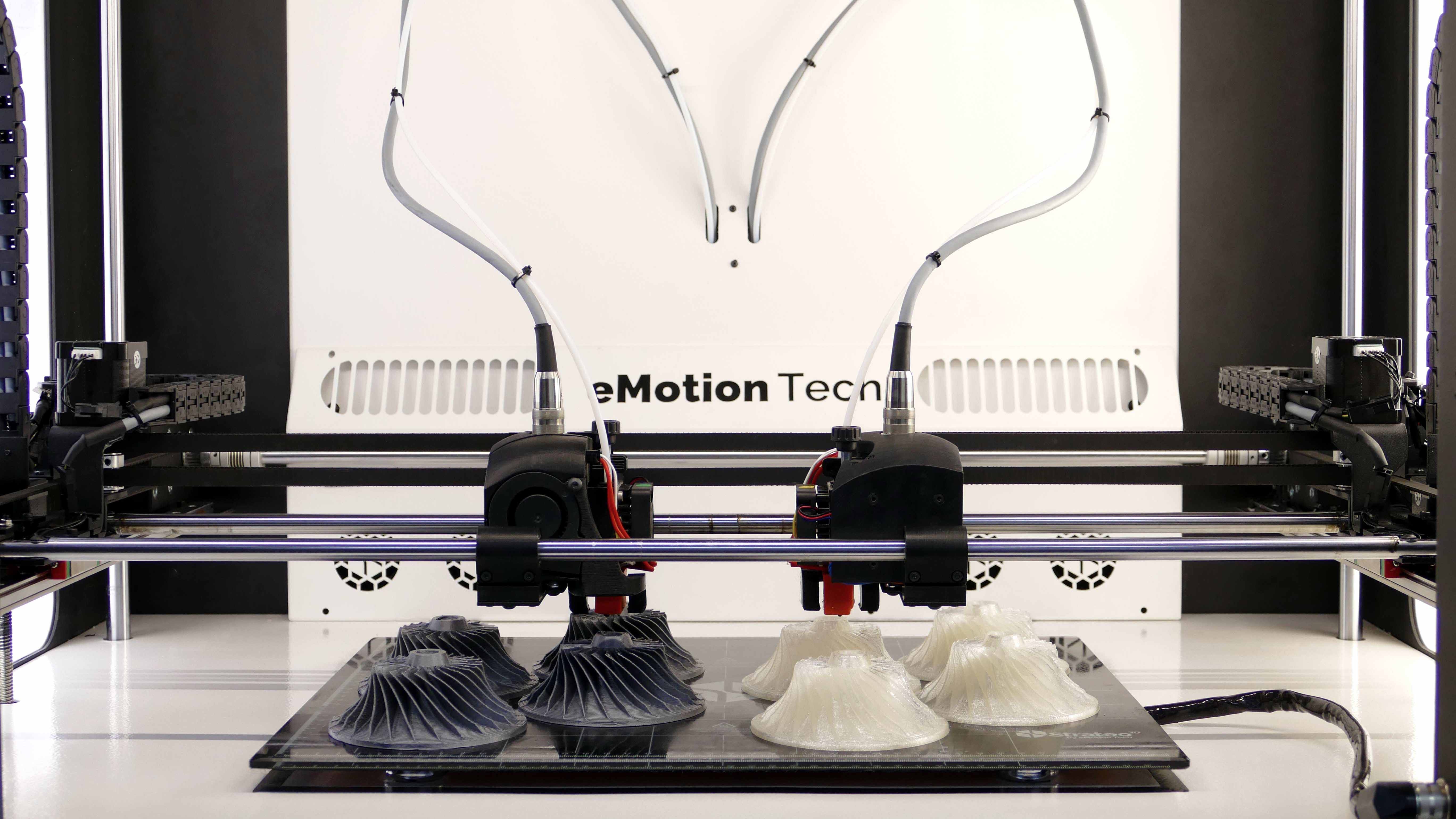
Additive manufacturing is a technology that uses the gradual accumulation of materials to create a solid model, which is a "bottom-up" manufacturing method compared to the traditional material removal cutting technology, also known as
3D printing manufacturing technology. It combines computer-aided design, material processing and molding technology, based on digital model data, through software and CNC system, resin materials, metal materials and medical biomaterials, etc., according to extrusion, sintering, fusion, light curing, injection, etc., layer by layer stacking, manufacturing technology to create a solid object.
For example: 3D printer printing implant guide , denture base, denture bracket, restoration model ......
Since the form and weight of the product is gradually shaped from nothing to something in the process of manufacturing the product, there is no reduction of material in the production process, but rather a gradual increase, so this technology is called additive manufacturing.
02 Additive manufacturing
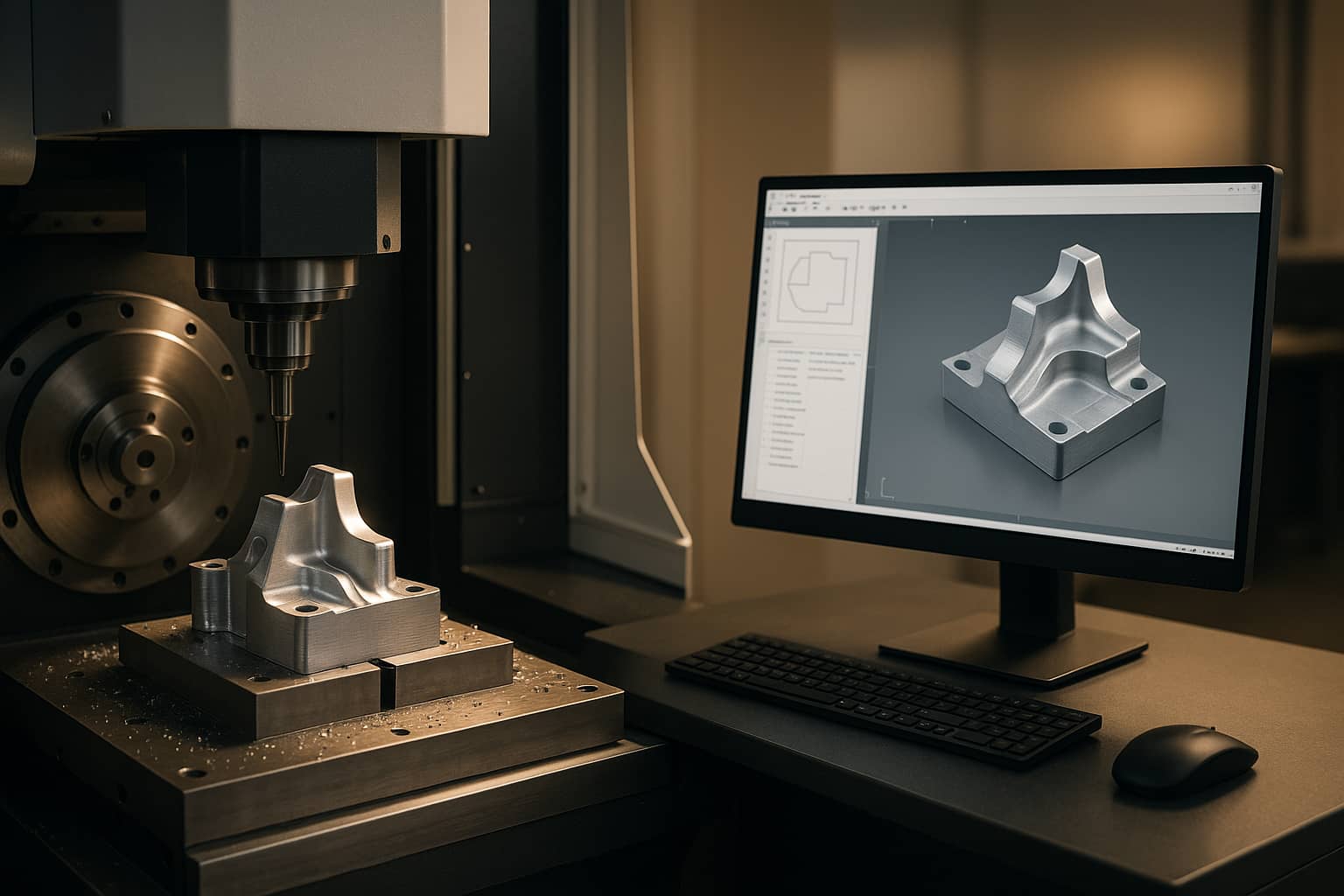
Subtractive manufacturing is a traditional machining method that uses tools to grind and cut materials to obtain the desired size, shape, and fineness.
Why is it subtractive manufacturing? Because the weight of the product after machining is reduced compared to the material before machining. For example, a piece of metal is fixed on a window, and the metal is turned into the desired size and shape by cutting with a tool head, and the "bead turning" used on the Internet is actually a kind of reduced material manufacturing.
03 Equivalent manufacturing
Equivalent manufacturing is a kind of manufacturing in which the size and shape of the material changes before and after processing, but its quality remains unchanged. For example, in ore smelting, there are many impurities in a piece of iron ore, and only by smelting it can iron be extracted from it. The mass of the iron ingot produced by smelting is reduced compared to the iron ore consumed, but the mass of the iron contained in the iron ore remains the same, so it is called equal material manufacturing.