

In the dynamic landscape of modern manufacturing, the injection molding industry stands at the crossroads of a profound transformation, driven by two overarching trends: digitization and sustainability. These trends are not only reshaping the operational paradigms of injection molding but are also redefining the industry's role in the global supply chain, making it more efficient, environmentally friendly, and competitive.
The advent of Industry 4.0 has ushered in a new era of smart manufacturing, and the injection molding industry is no exception. At its core, Industry 4.0 is about integrating digital technologies into every aspect of the production process, creating a seamless flow of data that enables real-time decision-making, optimization, and automation.
Injection molding machines are now equipped with an array of sensors that can monitor a multitude of process parameters in real-time. For instance, sensors can track mold temperature, injection pressure, cycle time, and energy consumption per cycle.
A study by Deloitte revealed that real-time monitoring allows manufacturers to reduce scrap rates by up to 30%.
This is crucial as even minor variations in these parameters can result in defective products. For example, a small fluctuation in mold temperature can cause uneven cooling, leading to warped parts.
The IoT has enabled injection molding machines to communicate with each other and with other devices in the factory ecosystem. This connectivity has broken down the traditional silos between machines, creating a unified production network.
McKinsey reports companies embracing IoT see 15-20% increase in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
For example, an injection molding machine can automatically signal an adjacent robotic arm to pick up a finished part once the molding cycle is complete. This increase in OEE is due to reduced downtime, better utilization of equipment, and improved coordination between different stages of the production line.

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are emerging as game-changers in the injection molding industry, bringing unprecedented levels of optimization and predictive capabilities.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of historical production data to identify the optimal process settings for different types of products. By considering factors such as material properties, mold design, and product specifications, AI can determine the ideal injection speed, pressure, and cooling time.
Automotive case study: 25% cycle time reduction and 10% quality improvement.
Machine learning models can predict when an injection molding machine is likely to experience a breakdown by analyzing data on machine vibrations, temperature, and energy consumption patterns.
GE reports up to 50% reduction in unplanned downtime.
This significant reduction in downtime not only saves costs associated with emergency repairs but also ensures a more consistent production schedule.

Digital twin technology is revolutionizing the way injection molding processes are designed, tested, and optimized. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical injection molding machine or process.
Engineers can use digital twins to simulate different injection molding scenarios before physically producing a prototype. This allows them to test and optimize the design of molds, predict potential manufacturing issues, and make necessary adjustments in the virtual environment.
PTC study: 50-70% reduction in physical prototypes.
For example, a consumer electronics company cut product development time by three months using digital twins for a new smartphone case.
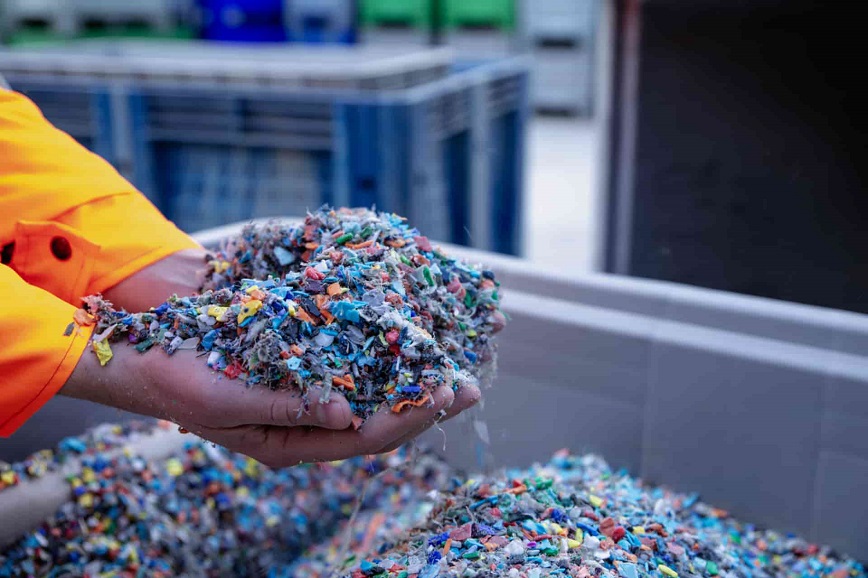

The injection molding industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact through sustainable materials.
The demand for biodegradable plastics like PLA and PHA is rising due to environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. These materials decompose naturally, reducing plastic waste.
Market projected to reach $7.9 billion by 2025 (MarketsandMarkets).
Many companies now use PLA-based injection-molded containers for food products as sustainable alternatives.
Recycling plastic waste for reuse in injection molding helps conserve resources and reduce landfill waste.
Ellen MacArthur Foundation: 50% recycled plastic use by 2030 could reduce carbon footprint by 20%.
Automotive manufacturers are using recycled plastics for interior components like dashboards and door panels.
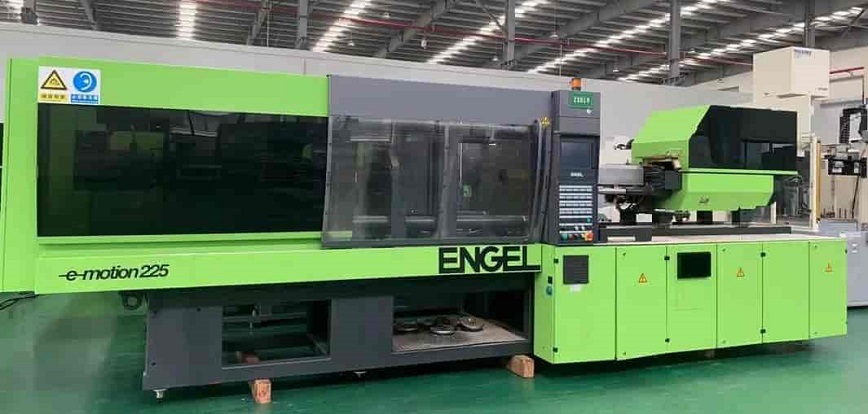

Newer injection molding machines feature energy-efficient technologies like servo-hydraulic systems that adjust power output based on process requirements.
Engel reports up to 50% energy savings with servo-hydraulic machines.
Process optimization through fine-tuning injection speed, pressure, and cooling time can reduce energy per cycle by 20%.
These trends are increasingly intersecting and reinforcing each other:
Digital energy management systems analyze consumption patterns to implement targeted savings. One European company reduced annual energy use by 15%.
Data analytics identifies root causes of scrap parts, enabling companies to decrease scrap rates by 20-30%.
60% of SMEs cite high costs as a barrier to adopting new technologies (American Mold Builders Association).
80% of companies report shortages in digital and sustainable manufacturing skills (Manufacturing Institute).
73% of consumers will pay more for sustainable products (Nielsen).
One Asian company achieved 20% production cost reduction over five years.
The injection molding industry is undergoing a remarkable transformation through digitization and sustainability. Digital technologies enable higher efficiency and quality, while sustainability initiatives reduce environmental impact. Companies embracing these trends will thrive in the competitive global manufacturing landscape.