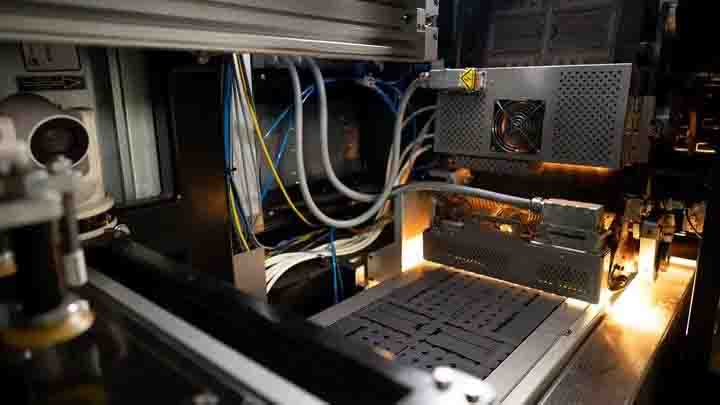
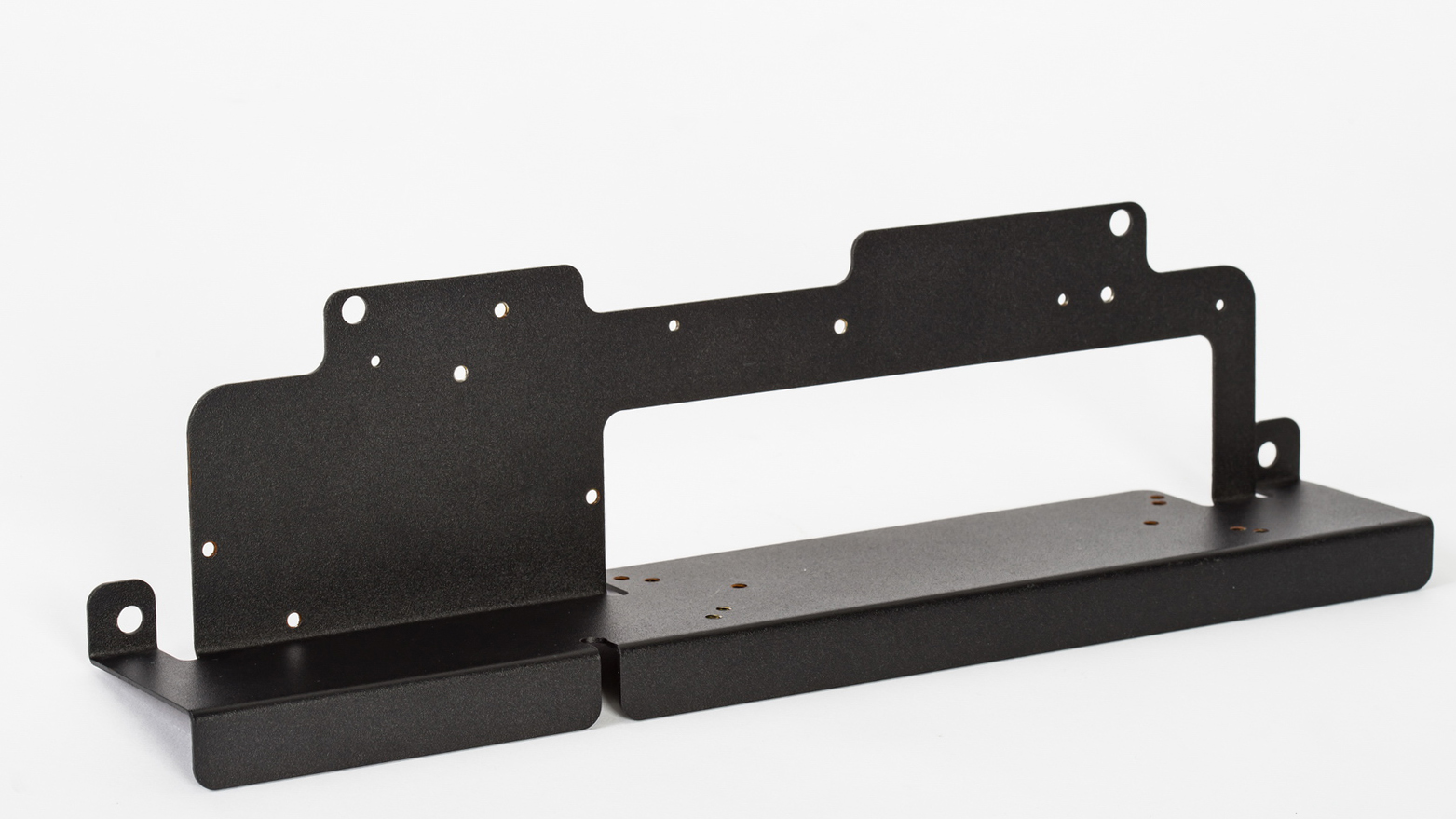










What Is 3D printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a technology based on digital model files, using powder metal or plastic and other bindable materials to construct objects by printing layer by layer. 3D printing is usually realized by using digital technology and material printer. It is often used in mold manufacturing, industrial design and other fields to make models, and then gradually used in the direct manufacturing of some products. There are already parts printed with this technology.
Materials must be suitable for application to be successful. With the development of products from conceptual and functional prototype design to production, the characteristics of any material become more and more important. However, material properties can only be evaluated when considering the manufacturing process. It is the combination of materials and processes that determine the characteristics..

1. SLA light curing rapid prototyping photosensitive resin
Milky white has good texture and strength, but its toughness is relatively small. Small and thin ones are prone to brittle fracture, but they are easy to be polished, electroplated and painted. Photosensitive resin consists of two parts: photoinitiator and resin. The amount of photoinitiator and diluent has an important influence on the curing speed and quality of photosensitive resin. When the dosage ratio of photoinitiator and diluent is appropriate, not only the curing speed is fast, but also the curing quality is good.
2. FDM melt deposition molding thermoplastic 3D printing material
Relatively speaking, the surface printing layer marks are obvious and rough. However, the material characteristics of good strength, high anti-collision and stable durability are conducive to accurate function test, mold and ideal material for producing finished products. The 3D printing materials used in this kind of 3D printing technology include industrial grade 3D printing materials and desktop grade 3D printer consumables.
3. SLS selective laser sintering powder
PA series nylon 3D printing materials: wear resistance, high strength and stiffness, good chemical resistance, excellent long-term constant behavior, high selectivity and detail analysis, biocompatibility, compliance with EN ISO 10993-1 and USP, compliance with EU plastics directive, approved for food contact. Pa3200gf nylon glass fiber material is also used for deep drawing molds or any other applications requiring specific stiffness, high thermal deformation temperature and low wear; Aluminum filled nylon materials are typically used in metal appearance and heat load parts. At present, desktop LS laser sintering PA12 nylon powder material is also an option.
4. 3D casting mold manufacturing materials
It is suitable for wax loss casting and sand casting. It can print high-precision parts, easily remove supporting materials, and there are a variety of materials to choose from. It can reduce the waste of materials in casting, save cost and speed up.
5. 3DP polyjet series 3D printing engineering plastics 3D printing materials
Multi nozzle jet cold light curing, can print high-precision small parts. Easy removal of support material. There are many different material choices (including soft glue), which are typically used in wax loss casting such as jewelry, precision machinery and electronic components, as well as the manufacturing of precision machinery, electronics and optical parts, with performance close to batch physical manufacturing.
6. Lom film layer superimposed 3D printing material
The main materials are paper, plastic film and metal foil. Rarely used in China.
7. DMLS, LSM laser sintered metal powder, EBM electron beam molten metal printing metal material
Titanium Ti64 titanium alloy, die steel MS1, stainless steel GP1, 17-4, 316, high temperature nickel alloy IN718, 625, magnesium aluminum alloy alsi10mg, CoCrMo cobalt chromium molybdenum alloy, cobaltchrome SP2 cobalt based cermet alloy, bronze, precious metals (including gold), etc.
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS): it can be used to build objects from almost any metal alloy. Direct metal laser sintering spreads a very thin layer of metal powder on the surface to be printed. The laser passes slowly and steadily through the surface to sinter the powder, and the inner particles of the metal fuse together, even if they are not heated to a fully molten state. An additional layer of powder is then applied and sintered to "print" one cross-section of the object at a time. After printing, the object will slowly cool down, and the excess powder can be recovered from the construction room and recycled. The main advantage of DMLS is that it produces objects without residual stress and internal defects, which is very important for metal parts under high stress (such as aerospace or automotive parts), and the main disadvantage is very expensive.
Selective laser melting (SLM): use high-power laser to completely melt each layer of metal powder, not just sintering, so that the printed object is very dense and solid. At present, this process can only be used for certain metals, such as stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, cobalt chromium alloy and aluminum. The high temperature gradient during SLM manufacturing will also lead to stress and dislocation in the final product, which will damage the physical properties.
Electron beam melting (EBM): very similar to selective laser melting, it can produce dense metal structure. The difference between the two technologies is that EBM uses an electron beam instead of a laser to melt metal powder. At present, electron beam melting can only be used for a limited number of metals. Although cobalt chromium alloy can also be used, titanium alloy is still the main raw material of this process. This technology is mainly used to manufacture parts for the aerospace industry.
Technical advantages: it can manufacture almost any geometry with high precision. A wide range of metals are used, including the lightest titanium alloy and the strongest nickel superalloy, which are difficult to process by traditional manufacturing technology. Mechanical properties can be comparable to forged metal, and can be machined, coated and treated like traditional metal parts.
www.mastars.com
Email: marketing@mastars.com
Tel: +86 755-88210690
Mobile: +86 181 0029 4997
Add: Building 6,Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China